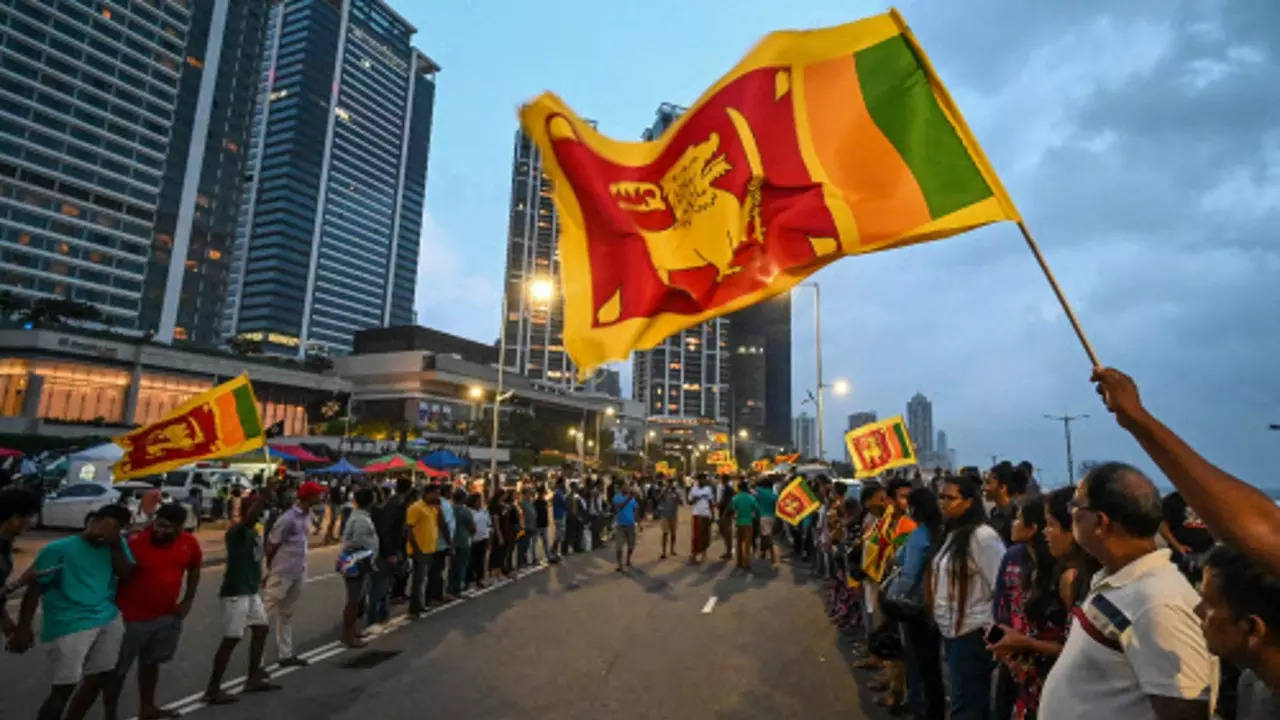
NEW DELHI: Sri Lanka's unprecedented economic crisis has only deepened further in the past few months, stemming from mismanaged government finances and ill-timed tax cuts in addition to the impact of Covid pandemic.
Diminishing forex reserves, huge piles of debt, devaluation of currency, rising inflation and a falling economy has compelled the people to struggle for items of basic necessity as well.
After weeks of anti-government protests, Mahinda Rajapaksa resigned from the post of Prime Minister, earlier this week.
Much of the public ire has been directed at Mahinda and his brother Gotabaya Rajapaksa -- who is the President of the island nation -- for leading the country into the economic crisis.
How crisis worsened
The crisis -- worst since Sri Lanka's independence from Britain in 1948 -- was caused in part by a lack of foreign currency. This meant that the country cannot afford to pay for imports of staple foods and fuel.
Consequently, the country's inability to pay for basic necessity items lead to acute shortages and pushed up prices to record highs.
Critics say the roots of the crisis lie in economic mismanagement by successive governments that created and sustained a twin deficit - a budget shortfall alongside a current account deficit.

"Sri Lanka is a classic twin deficits economy," said a 2019 Asian Development Bank working paper. "Twin deficits signal that a country's national expenditure exceeds its national income, and that its production of tradable goods and services is inadequate."
But the current crisis was accelerated by deep tax cuts promised by Rajapaksa during a 2019 election campaign that were enacted months before the Covid-19 pandemic, which wiped out parts of Sri Lanka's economy.
With the country's lucrative tourism industry and foreign workers' remittances sapped by the pandemic, credit ratings agencies moved to downgrade Sri Lanka and effectively locked it out of international capital markets.
In turn, Sri Lanka's debt management programme, which depended on accessing those markets, derailed and foreign exchange reserves plummeted by almost 70 per cent in 2 years.
The Rajapaksa government's decision to ban all chemical fertilisers in 2021, a move that was later reversed, also hit the country's farm sector and triggered a drop in the critical rice crop.
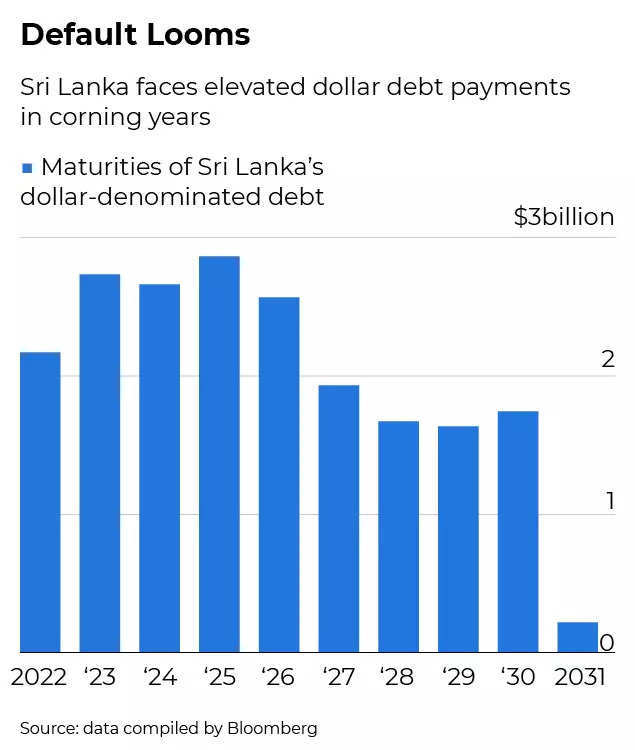
The country’s foreign reserves have dropped below $50 million. This has forced the government to suspend payments on $7 billion in foreign debt due this year, with nearly $25 billion due by 2026 out of a total of $51 billion.
The country is now very close to bankruptcy.
How crisis disrupted life
For months, people in the country have had to wait in long lines to buy essential items because as forex crisis led to acute shortages in imported food, medicines and fuel.
Job losses have become a common phenomenon in almost every household. Besides, fall in earning has led to rise in poverty rates.
According to World Bank data, the share of the poor based on a daily income of $3.20 was estimated to have grown to 11.7 per cent in 2020 - or by more than half a million people - from 9.2 per cent a year before.
The government had identified 5 million families with "fragile financial status of low-income households" and provided them a Rs 5,000 allowance during the Covid-19 lockdowns. But that helped only briefly.
The latest economic crash - compounded by the Russia-Ukraine conflict that has led to a steep hike in oil prices - served another gut punch, and making scenes of desperation and panic more and more common among people.
Shortages have scaled to such heights that examinations for millions of students in the country had to be postponed due to lack of paper and ink.
As oil prices soared during the Russia-Ukraine conflict, Sri Lanka’s fuel stocks are running out. Authorities have announced countrywide power cuts will increase to about four a day because they can’t supply enough fuel to power generating stations.
Fuel shortages have led to long lines at petrol stations and rolling power cuts across much of the country. A serious shortage of diesel has shut multiple thermal power plants causing rolling power cuts across the nation.
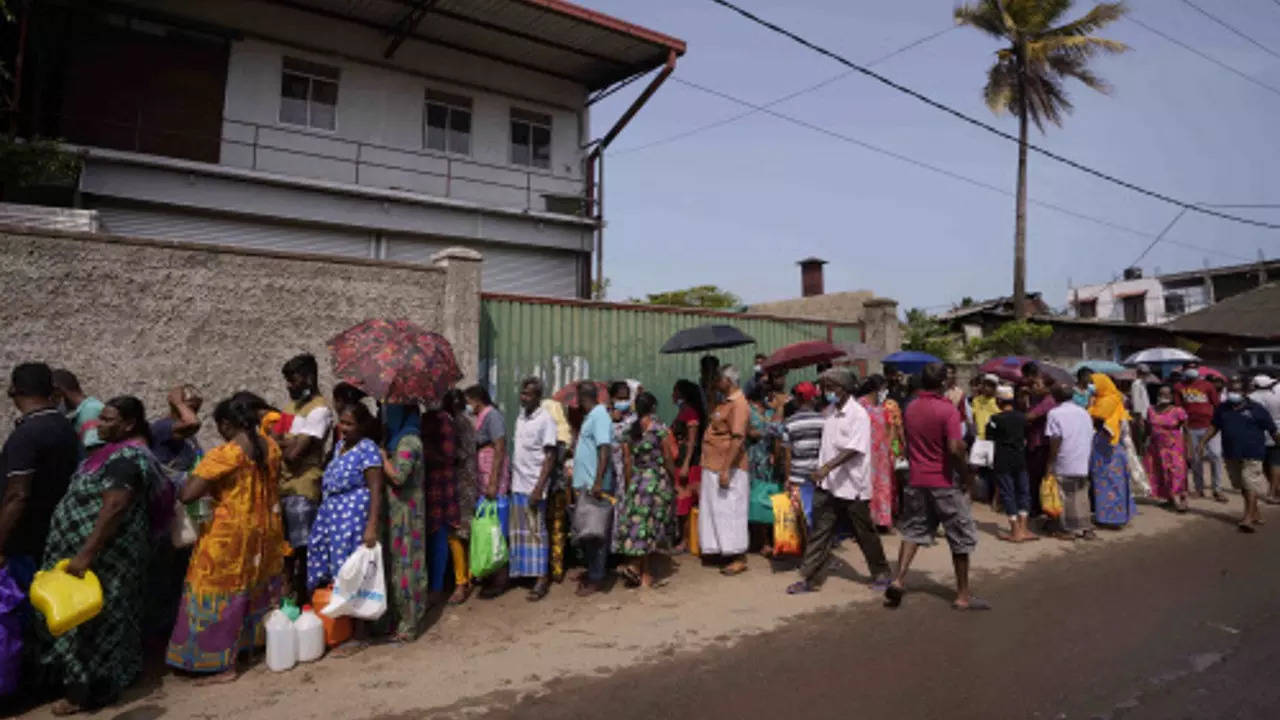

People wait in a queue to buy kerosene oil for cooking outside a fuel station in Colombo (Photo: AP)
Fuel prices have also been increased frequently with petrol up by 92 per cent and diesel by 76 per cent since the beginning of the year. People in the country are also dealing with shortages and soaring inflation, after the country steeply devalued its currency in March.
The sudden rise in prices of commodities has pushed up inflation to record levels. In April, the country's inflation figure stood at nearly 30 per cent -- way above its' central bank's target range of 4-6 per cent over the medium term.
Meanwhile, Sri Lankan rupee depreciated against the US dollar by 33 per cent during the year up to April 1, 2022. Given the cross currency exchange rate movements, the Sri Lankan rupee depreciated against the Indian rupee by 31.6 per cent, the euro by 31.5 per cent, the pound sterling by 31.1 per cent and the Japanese yen by 28.7 per cent during this period.
Is politics to be blamed?
As Sri Lanka battles a crippling economic crisis, it’s hard to overstate the influence of the Rajapaksa clan in all this. Gotabaya, who won office in the November 2019 presidential election, appointed his brother, Mahinda, as prime minister.
Mahinda first came to power in 2004, initially as prime minister and then as president. At the time, Gotabaya was defence secretary and was notorious for his role in the 2009 operation to end the civil war with Tamil rebels.
The Rajapaksas were out of power briefly from 2015, when Maithripala Sirisena and Ranil Wickremesinghe led the country, until Wickremesinghe was removed from his post in 2018, sparking a constitutional crisis.
The Rajapaksas’ party won a landslide victory in the August 2020 general election, and quickly restored sweeping executive powers to the presidency that had been previously curbed.
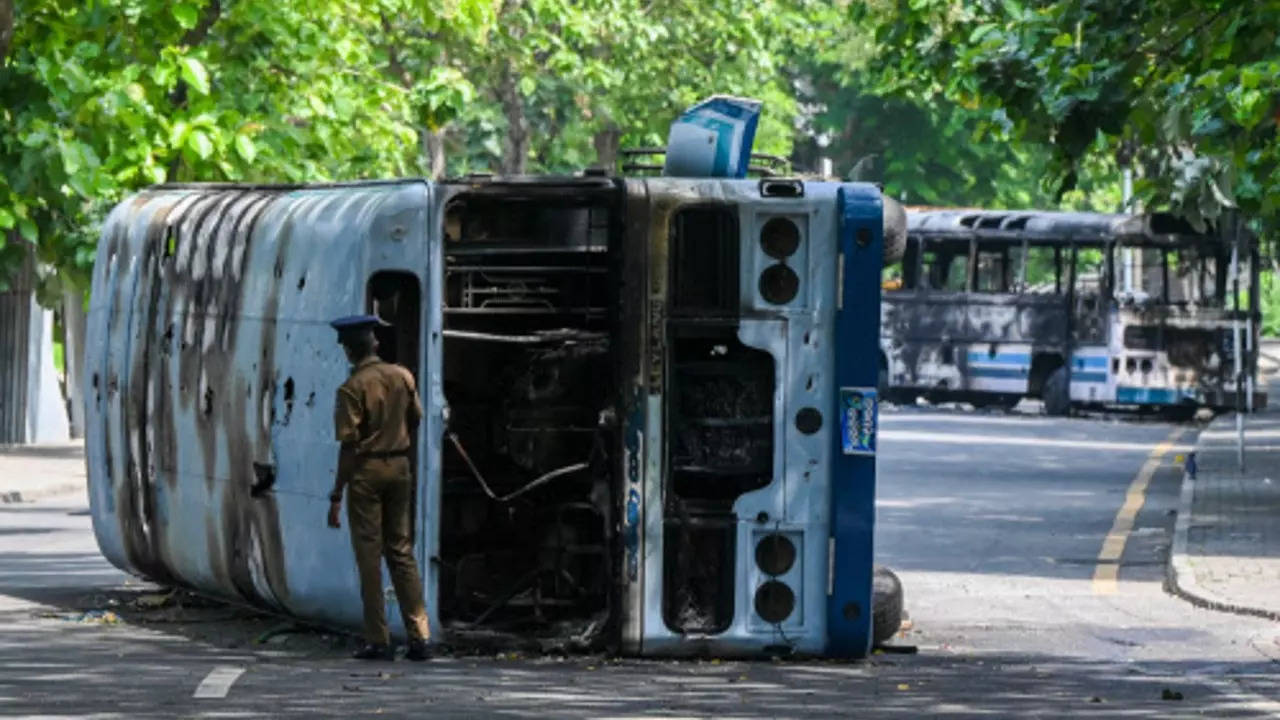

A policeman inspects a bus burnt during demonstrations against the government over Sri Lanka's crippling economic crisis (Photo: AFP)
When the economy started dwindling, the Rajapaksa government not only resisted aid from neigbouring countries but also held off talks with International Monetary Fund (IMF).
For months, opposition leaders and some financial experts urged the government to act, but it held its ground, hoping for tourism to bounce back and remittances to recover.
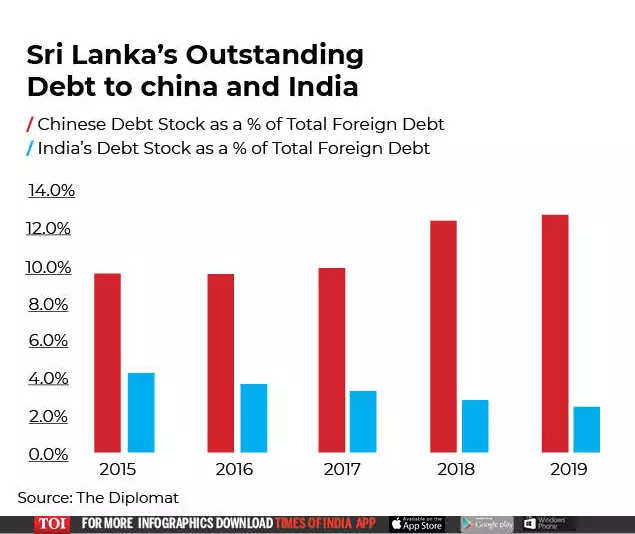
Eventually, aware of the scale of the brewing crisis, the government did seek help from countries including India and China, regional superpowers who have traditionally jostled for influence over the strategically located island.
In all, India has provided support worth over $3.5 billion to the island nation this year.
Earlier in 2022, President Rajapaksa asked China to restructure repayments on around $3.5 billion of debt owed to Beijing, which in late 2021 also provided Sri Lanka with a $1.5 billion yuan-denominated swap.
In a statement today Central Bank of Sri Lanka's governor Nandalal Weerasinghe said: "If we don't have political stability, very soon we will run out of what little petrol and diesel left. At that point people will get on the streets to protest peacefully or violently."
'Collapse beyond redemption'
Sri Lanka's economy will "collapse beyond redemption" unless a new government is appointed within two days to restore political stability, the central bank chief said.
He said the latest wave of mob violence derailed the bank's recovery plans, and the resignation of the prime minister on Monday and the lack of a replacement were complicating matters.
He said political stability was vital to implementing economic reforms aimed at addressing the country's debt crisis and the acute shortage of foreign exchange to import essentials.
"If there is no government in the next two days, the economy will completely collapse and no one will be able to save it," Central Bank of Sri Lanka governor Nandalal Weerasinghe said.
Shortly after taking over last month as the bank's chief, Weerasinghe announced defaulting on Sri Lanka's $51 billion external debt saying the country had no money to pay its creditors.
He almost doubled interest rates and allowed the rupee to depreciate rapidly to ensure better foreign exchange liquidity in the commercial banks.
"I will resign if there is no immediate action to form a government," Weerasinghe said.
What's next for Sri Lanka
To bring Sri Lanka out of this deep economic crisis, the first step would be to have a stabilised government at the Centre.
The Cabinet got dissolved automatically after resignation by Mahinda Rajapaksa. At present, the country is without a prime minister.
President Rajapaksa has sought support from all political parties in parliament to form a unity government, an offer that many, including the ruling alliance's allies, have declined.
Thousands of protesters, some of whom have camped out on the streets for weeks to the chants of "Gota(baya) go home", also want the president to step down.
However, if the president also resigns while there is no prime minister, the Parliament speaker will become interim president for 1 month, during which Parliament will have to select a member to become president until an election can be held.
Some Sri Lankan business groups are leaning on the country's politicians to quickly find a solution, as amid an escalation of violence. Houses and cars have been torched in other parts of the country.
The president could attempt to form a unity government, but it will likely be difficult to convince opposition members to join.
In the 45 years that Sri Lanka has been ruled by an executive presidential system, there has been one failed attempt to oust a president. The constitution gives the president wide powers as commander-in-chief of the armed forces, head of the Cabinet and powers to appoint the chief justice, police chief and others.
The president, despite his extensive powers, still needs a prime minister and Cabinet to carry out executive functions.
The ongoing uncertainty over the president’s next moves and the administrative vacuum have raised fears of a military takeover, especially if violence escalates.
(With inputs from agencies)







