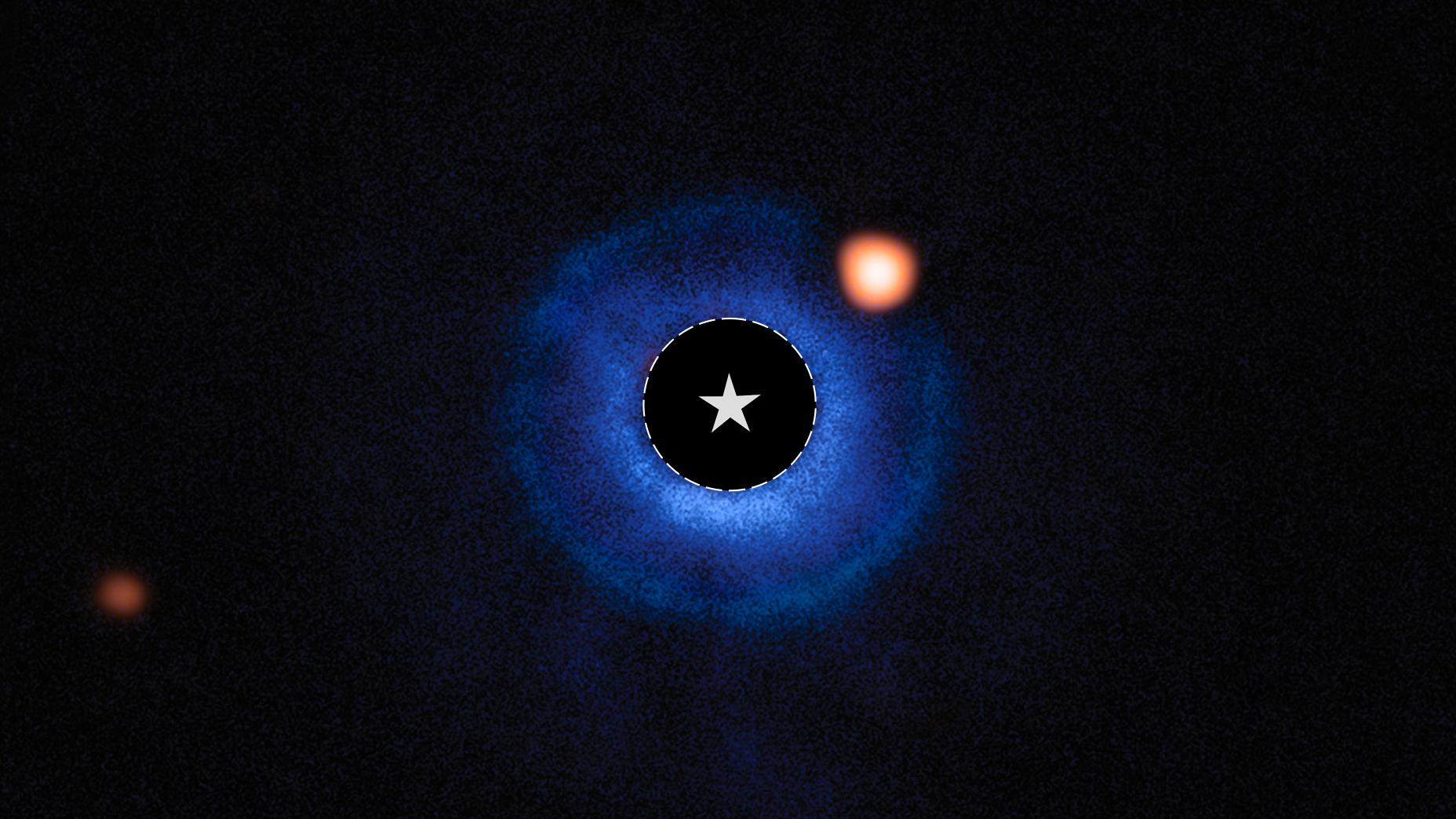
Photographers often can't get enough light – but by blocking out some light, the largest telescope launched into space has photographed what could be its first previously undiscovered planet. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has photographed what researchers believe is a new exoplanet, dubbed TWA 7 b.
While the new exoplanet is estimated to be around the mass of Saturn, the TWA 7 b is believed to be the lightest planet ever seen using the Mid-Infrared Instrument imaging. The exoplanet orbits the star TWA 7, around 34 light-years from Earth.
One of the challenges in locating new, distant planets is that the stars they orbit typically give off so much light that the planet’s dimmer light is lost in the star’s brightness. The James Webb Space Telescope compensates for this using the coronagraph technique.
A coronagraph is a technique that requires blocking off light from a star in order to see objects otherwise lost in the star’s brightness. By blocking off the star's brightness – the black circular gap marked by the star icon in the photograph above – scientists were able to see evidence of TWA 7 b.
The new exoplanet hasn’t yet been confirmed – NASA notes that there’s a small chance that the object in the photograph is a background galaxy rather than an exoplanet. But as scientists continue to research the find, the evidence points to the shape being the James Webb Telescope’s first discovery of a previously unknown planet.
The telescope’s ability to photograph the mid-infrared has enabled the James Webb to aid scientists in studying distant but known planets for the last three years. Now, the technology inside the telescope has allowed for the discovery of what appears to be an undiscovered planet.
The James Webb Telescope – the largest ever to launch into space – is designed to detect light outside what humans can see with the naked eye. The near and mid-infrared capabilities of the telescope are helping scientists explore what NASA describes as otherwise hidden regions of space.
Infrared technology is key to photographing distant space objects through clouds of dust, as well as low-energy stars and planets like brown dwarfs and young protostars.
The infrared technology inside the James Webb has allowed the TWA 7 b to be detected through the three dust rings that surround that system’s star. The exoplanet is positioned in a gap in the dust disks, leading scientists to theorize that the planet could be what’s shaping the dust structures.
While ongoing work is needed to confirm the object as a planet and record additional observations, the photograph also illustrates Webb’s potential to find previously unseen planets.
The research was published earlier this week in Nature.
You may also like
Browse the best lenses for astrophotography or find inspiration in these star photography tips.