- In today’s CEO Daily: Nick Gordon on Nintendo’s astonishing 98% employee retention rate.
- The big story: Netflix to acquire Warner Bros. Discovery studios.
- The markets: Mostly up.
- Plus: All the news and watercooler chat from Fortune.
Good morning. When experienced employees leave–whether they get laid off, or jump ship for a better opportunity–they take their years, if not decades, of experience with them. Over time, the company loses that institutional knowledge.
But what happens when a company excels at keeping its workers?
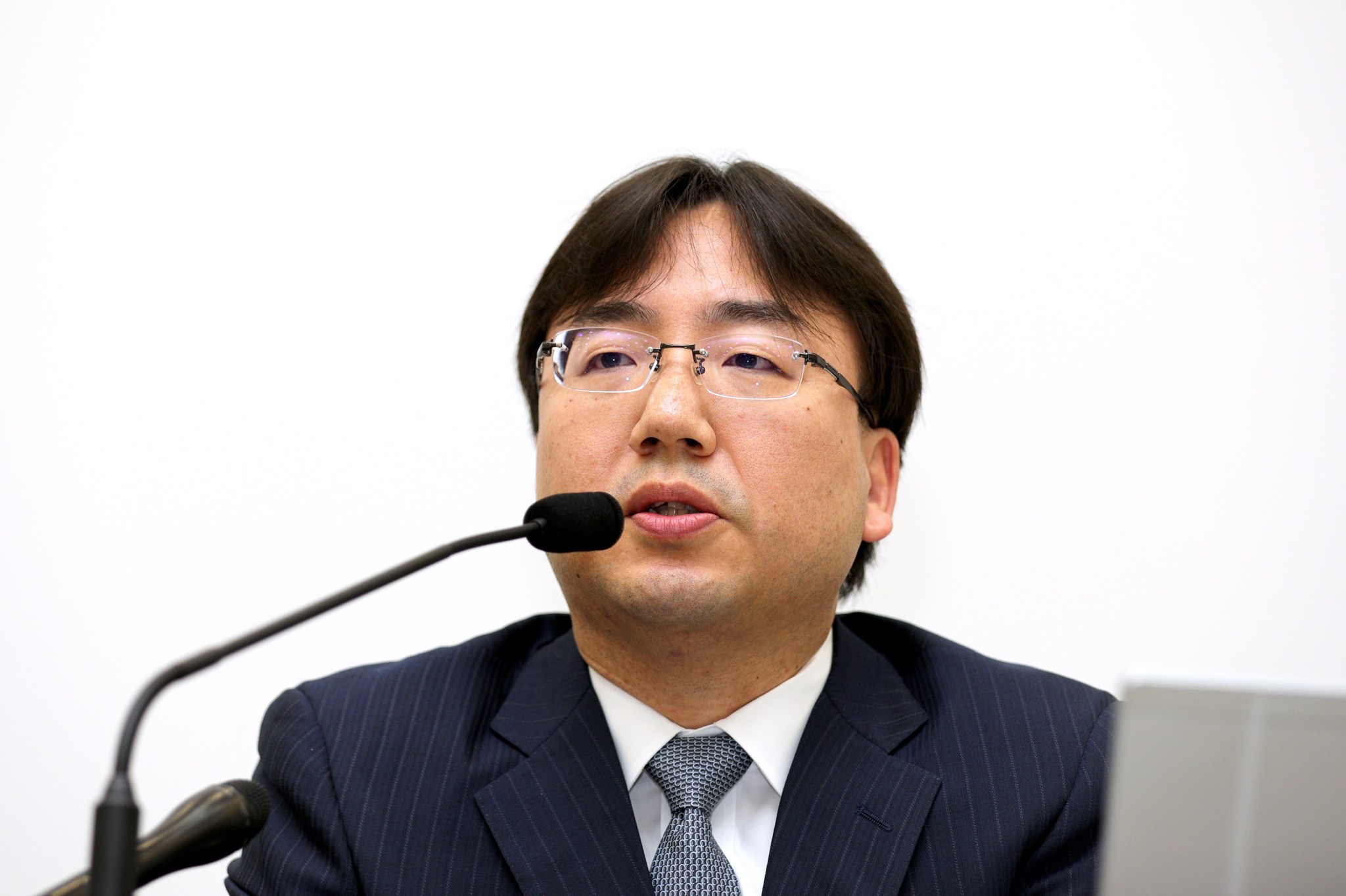
Nintendo, the Japanese video game giant, is an example. Its Japanese employees spend an average of 15 years at the company, which boasts a yearly retention rate of 98%. That’s not just better than the layoff-prone video game industry, it’s better than most of Japan. The average Japanese worker spends 11 years at their company; in the U.S., that number is closer to four.
“The people who first made Nintendo’s hits are still working at the company,” Keza MacDonald, the author of Super Nintendo, a forthcoming book about the developer, told me recently. “For the last 50 years, these people have been passing down knowledge and training up a new generation of Nintendo creatives.”
Both Nintendo’s business and creative leaders have long tenures at the company. Current president Shuntaro Furakawa joined the company in 1994 as an accountant. Shigeru Miyamoto, the brains behind franchises like “Super Mario” and “The Legend of Zelda,” joined as a staff artist in 1977.
There is a risk that companies that rely too much on institutional knowledge get stuck in their ways. Yet Nintendo, according to MacDonald, has combined institutional knowledge with fresh ideas to continuously replenish its pipeline of fun games: “It’s not like the oldest guy gets to decide what’s a good idea and what isn’t. Everyone puts ideas in.”
Nintendo has its share of flops, failed experiments, and puzzling business decisions–as does every firm. Yet the company maintains its share of the highly competitive video game industry against bigger, deeper-pocketed rivals like Sony and Microsoft.
The few designers who’ve left Nintendo still have fond feelings about their time there. As Lee Schuneman, a former Nintendo game designer and now Efekta Education Group’s chief product officer, told our Brainstorm Design audience this week, “I got to work with some of the most talented game designers in the world, including people like [Shigeru Miyamoto] at Nintendo, and [learn] a whole range of lessons about how to make playful experiences.”
That goodwill may be the result of Nintendo avoiding the industry’s boom-bust churn and valuing the expertise its workforce accumulates.
Nintendo “is still, to this day, making games differently from everyone else,” MacDonald says. You can check out the rest of our mainstage sessions from Brainstorm Design here.—Nicholas Gordon
Contact CEO Daily via Diane Brady at diane.brady@fortune.com