Earth's orbital environment is becoming increasingly crowded. Thousands of satellites—many of them inactive, damaged, or out of fuel—now circle the planet alongside fragments of debris from past collisions.
As more and more satellites enter orbit, one of the biggest questions becomes: how can these satellites approach and maneuver around each other safely? To answer that question, Luxembourg-based companies LMO and ClearSpace carried out a carefully designed simulation using the European Space Agency's Guidance, Navigation and Control Rendezvous, Approach and Landing Simulator (GRALS).
What is it?
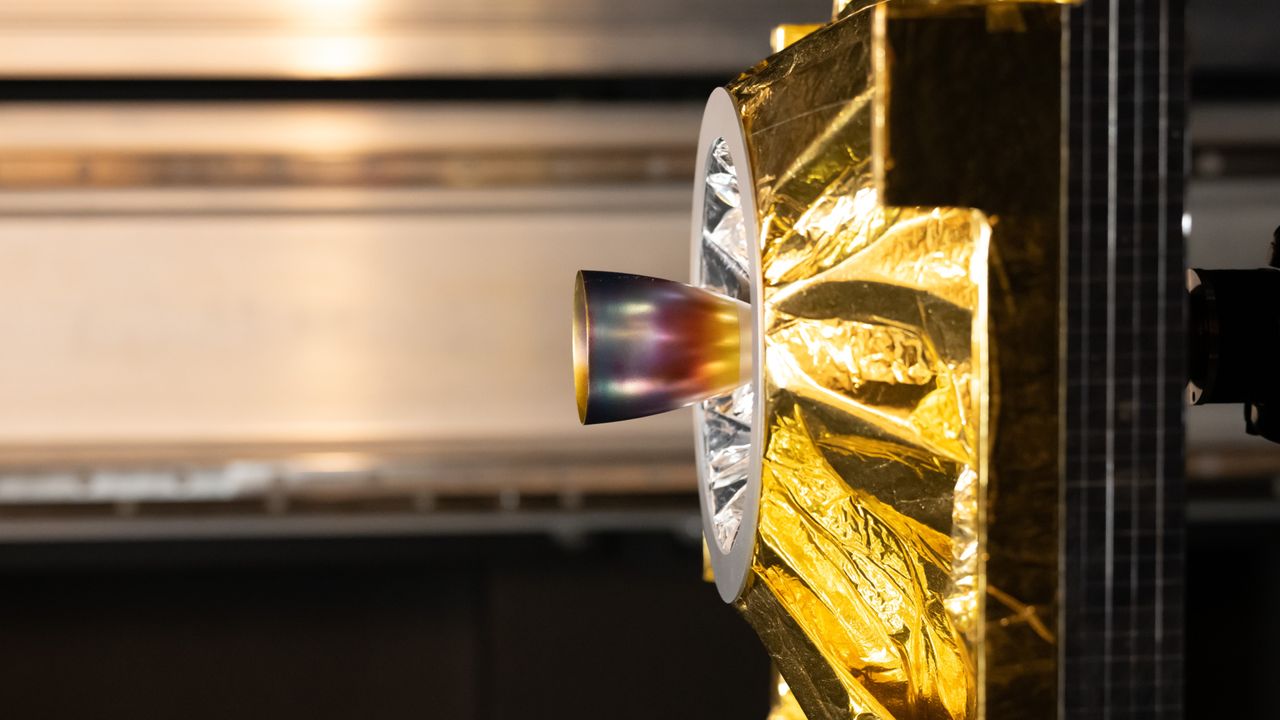
GRALS is part of ESA's Guidance, Navigation and Control Test Facilities and is built to recreate close-proximity operations in space with remarkable realism. The satellite model shown in this image was developed by ClearSpace to replicate the geometry, materials, and visual complexity of real satellites.
Its crinkled gold thermal insulation, metallic structures, and the cup-shaped reflective thruster are not just aesthetic details but critical features that influence how light behaves in space and how cameras perceive an object during a rendezvous.
To ensure reliability, engineers combine computer-generated imagery used to train AI systems with physical testing on increasingly realistic models. Smaller models simulate long-range approaches, while larger, high-fidelity replicas like the one shown are used to test the most delicate, close-range phases of a rendezvous.
Where is it?
This photo was taken at the ESA's technical center, ESTEC, in the Netherlands.
Why is it amazing?
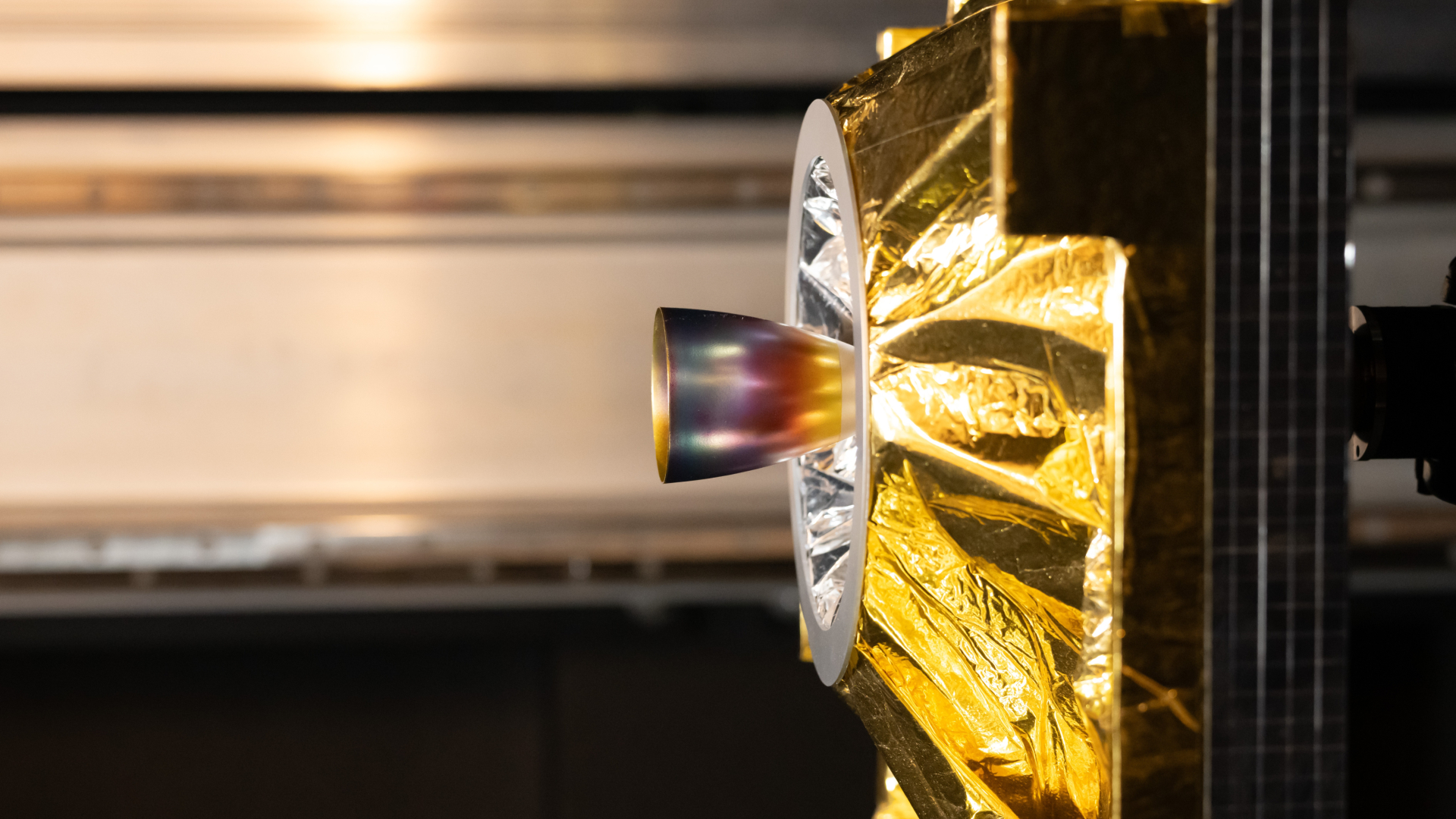
The thousands of satellites orbiting Earth pose growing risks to operational spacecraft and to the long-term sustainability of space activities. Before a spacecraft can refuel, repair, or safely deorbit another satellite, it must be able to see, identify, and approach its target with exceptional accuracy. Vision-Based Navigation systems are key to making this possible. Much like self-driving cars rely on cameras and AI to interpret their surroundings, VBN-equipped spacecraft must interpret light, shadow, reflections, and rapidly changing viewpoints in the harsh environment of space.
Facilities like GRALS play a critical role in bridging the gap between theory and reality. By testing real hardware against realistic satellite models under space-like lighting conditions, engineers can expose weaknesses, validate AI training, and build confidence that autonomous systems will behave safely once deployed in orbit.
Want to learn more?
You can learn more about satellite crowding and space junk.







