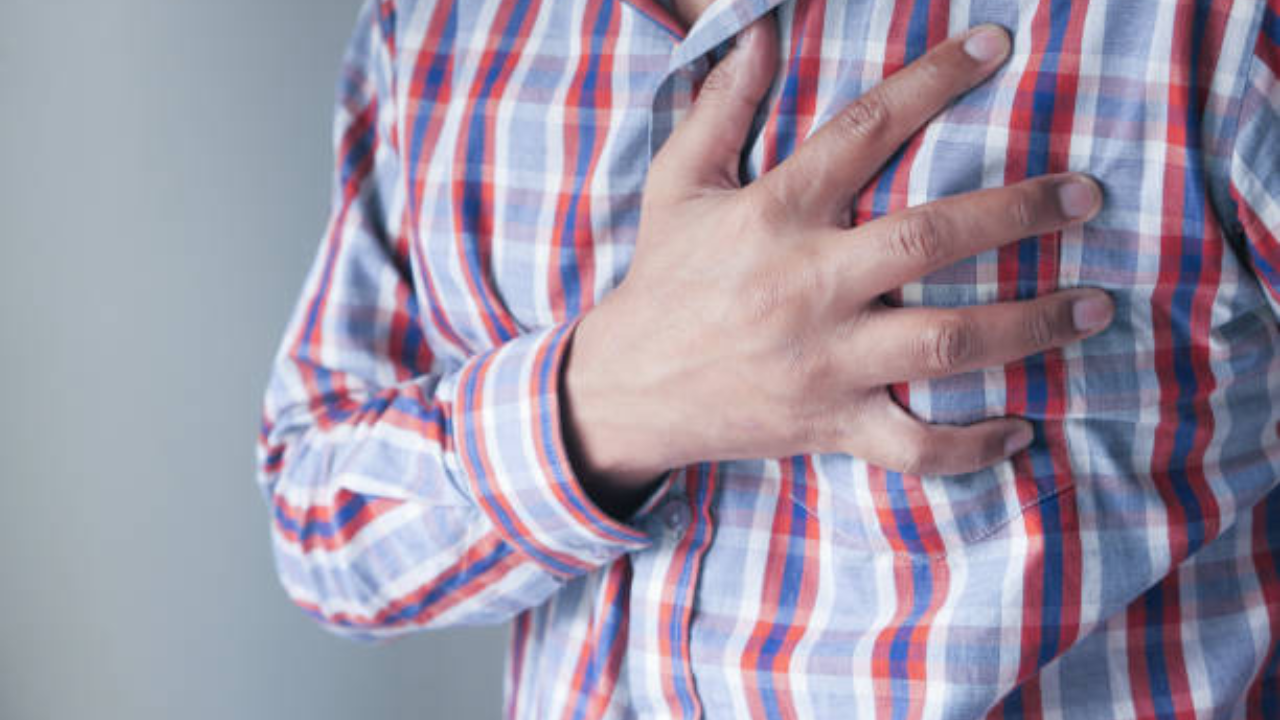
While often used interchangeably in casual conversations, cardiac arrest and heart attack are distinctly different medical emergencies. Understanding the nuances between these conditions is crucial, as it can make a life-or-death difference.
Cardiac Arrest: An electrical malfunction
Cardiac arrest is a sudden condition when a person's heart unexpectedly stops beating. It is primarily caused by a disturbance in the heart's electrical system, resulting in arrhythmias. These fatal arrhythmias are notably severe, with a survival rate of only 15%. Despite its severity, the incidence of cardiac arrest is rare, with a rate of 0.1%.
Dr. Niranjan Hiremath, a leading cardiovascular and aortic surgeon at Apollo Indraprastha, states, "Cardiac arrest is almost non-preventable, but a detailed cardiac check-up at the age of 18 can detect 'silent' structural cardiac abnormalities, potentially preventing future catastrophic events."
When someone experiences a cardiac arrest, it's paramount to start immediate CPR. If available, an automated external defibrillator (AED) can be used to administer a shock and attempt to bring the heart back to its regular rhythm. Following these immediate measures, it's essential to address the root causes of the cardiac arrest, which often involves consultation with an electrophysiologist.
Heart Attack: A circulation crisis
In contrast, a heart attack, known medically as a myocardial infarction, occurs when there's a sudden interruption in blood flow to a part of the heart muscle. This interruption, often due to a blockage, results in injury or death to the affected heart muscle tissue.
The implications of a heart attack are severe but have a notably higher survival rate of around 95% when treated promptly. After the onset of a heart attack, the patient typically has a window of roughly 60 minutes to reach a medical facility to undergo life-saving procedures that address the blockages.
Treatment options for a heart attack include thrombolysis (clot dissolving), angioplasty, and stenting. For patients with multiple blockages, consultation with both a cardiologist and cardiac surgeon is necessary, as coronary artery bypass surgery might be recommended.
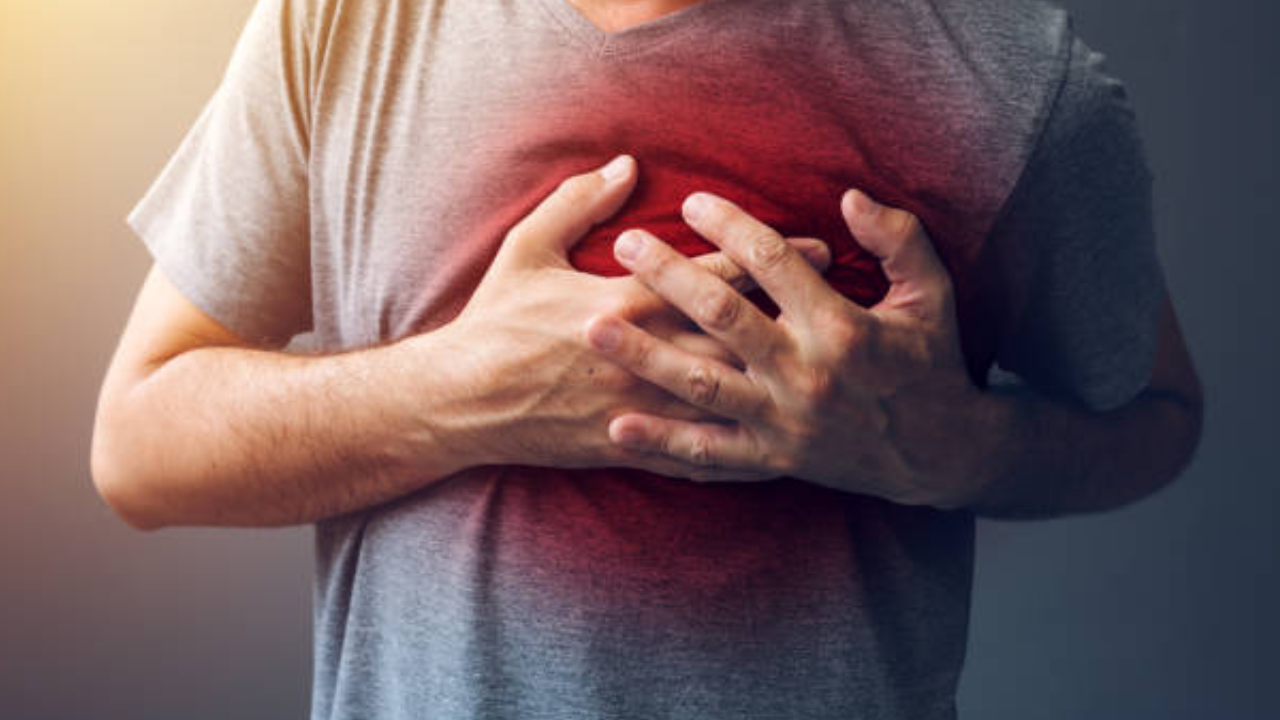

Prevention is always better than cure, especially concerning heart attacks. These can often be prevented by making lifestyle changes and addressing risk factors in a timely manner. Regular cardiac check-ups after the age of 35 are advised to detect and manage potential risks.
Differentiating emergencies
To quickly differentiate between the two:
1. Cardiac arrest: Sudden cessation of the heartbeat due to electrical disturbances, requiring immediate CPR and potentially an AED shock.
2. Heart attack: Death or injury to heart muscle caused by a lack of blood flow, allowing for roughly an hour to get to a hospital for treatment.
In conclusion
Both cardiac arrest and heart attacks are grave medical emergencies requiring rapid response. Awareness of the differences between the two can guide crucial first-response actions, ultimately saving more lives.
By seeking preventative care and regular check-ups, individuals can detect potential risks early and make informed decisions about their heart health, thus reducing the chances of either medical emergency.
Read Also:
(Dr Niranjan Hiremath is a senior consultant cardiovascular, aortic surgeon and the surgical lead of the Apollo Hospital)
Immediate ban imposed on serving food wrapped in newspapers: Here's why it can be dangerous







