Over the past three months, shares of Hallador Energy (NASDAQ:HNRG) rose by 65.56%. Before having a look at the importance of debt, let us look at how much debt Hallador Energy has.
Hallador Energy's Debt
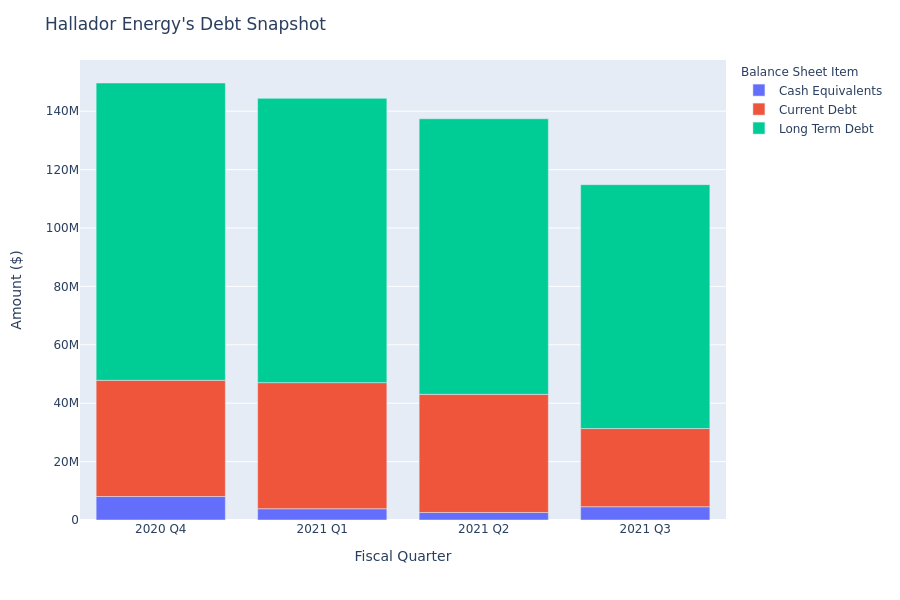
Based on Hallador Energy's balance sheet as of November 8, 2021, long-term debt is at $83.52 million and current debt is at $26.77 million, amounting to $110.30 million in total debt. Adjusted for $4.55 million in cash-equivalents, the company's net debt is at $105.75 million.
Let's define some of the terms we used in the paragraph above. Current debt is the portion of a company's debt which is due within 1 year, while long-term debt is the portion due in more than 1 year. Cash equivalents include cash and any liquid securities with maturity periods of 90 days or less. Total debt equals current debt plus long-term debt minus cash equivalents.
Shareholders look at the debt-ratio to understand how much financial leverage a company has. Hallador Energy has $363.08 million in total assets, therefore making the debt-ratio 0.3. Generally speaking, a debt-ratio more than one means that a large portion of debt is funded by assets. As the debt-ratio increases, so the does the risk of defaulting on loans, if interest rates were to increase. Different industries have different thresholds of tolerance for debt-ratios. A debt ratio of 25% might be higher for one industry and average for another.
Importance Of Debt
Debt is an important factor in the capital structure of a company, and can help it attain growth. Debt usually has a relatively lower financing cost than equity, which makes it an attractive option for executives.
However, due to interest-payment obligations, cash-flow of a company can be impacted. Equity owners can keep excess profit, generated from the debt capital, when companies use the debt capital for its business operations.
Looking for stocks with low debt-to-equity ratios? Check out Benzinga Pro, a market research platform which provides investors with near-instantaneous access to dozens of stock metrics - including debt-to-equity ratio. Click here to learn more.