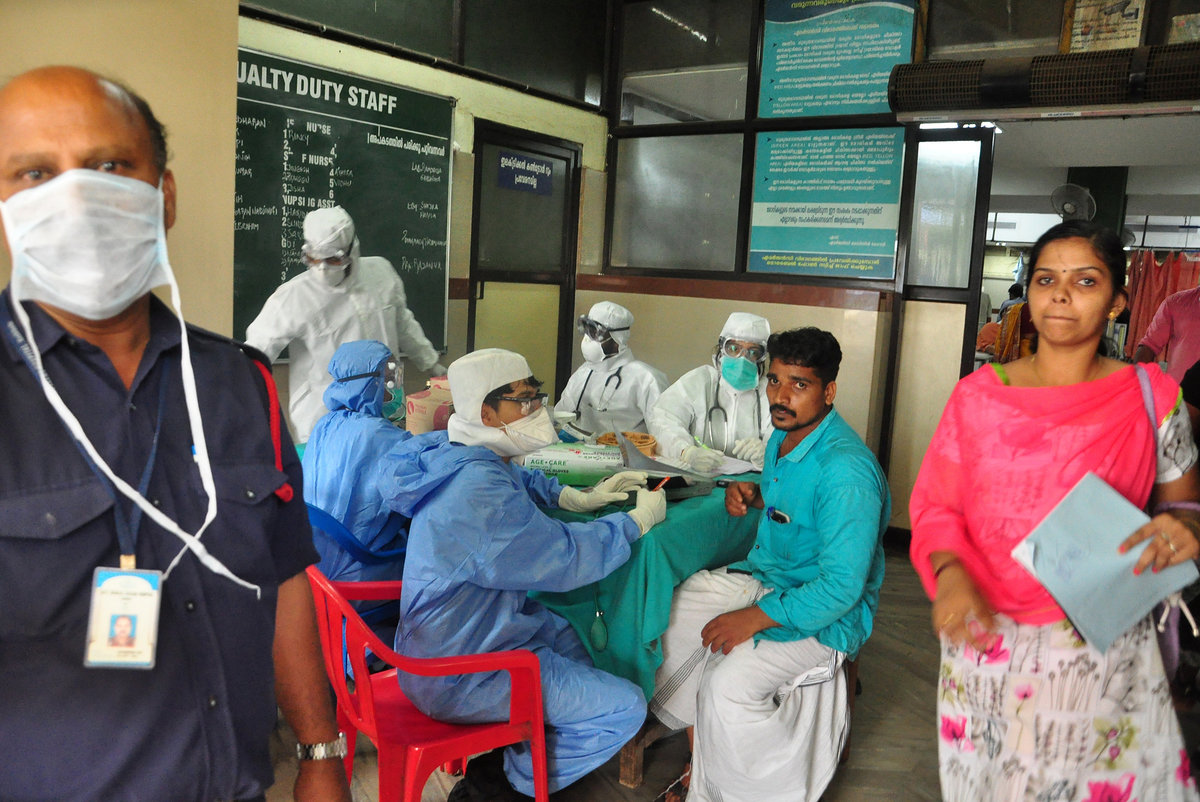
KOCHI/MUMBAI (Reuters) - Indian health officials were checking on Wednesday if a rare, brain-damaging virus had spread to a second state after two suspected cases reported in southern Karnataka, as the death toll in adjacent Kerala, where the outbreak began, rose to 11.
The world's second most populous country suffers hundreds of deaths from infectious diseases every year because of weak disease surveillance and infection control systems, leading health experts to worry about the risks of such outbreaks.

There is no vaccine for the Nipah virus, carried by fruit bats and spread through contact with bodily fluids, the World Health Organization (WHO) says. Treatment for the virus, which has a mortality rate of about 70 percent, is supportive care.
Symptoms of the virus surfaced in a 20-year-old woman and a 75-year-old man in the port city of Mangalore after they traveled to neighboring Kerala and had contact with infected patients, said Rajesh B.V., a health official in Karnataka.
"They are not confirmed Nipah cases yet, so there is no need to panic," he said by telephone. "The situation is under control."

The patients are being treated and samples of their blood have been sent for screening, with results expected by Thursday, he added.
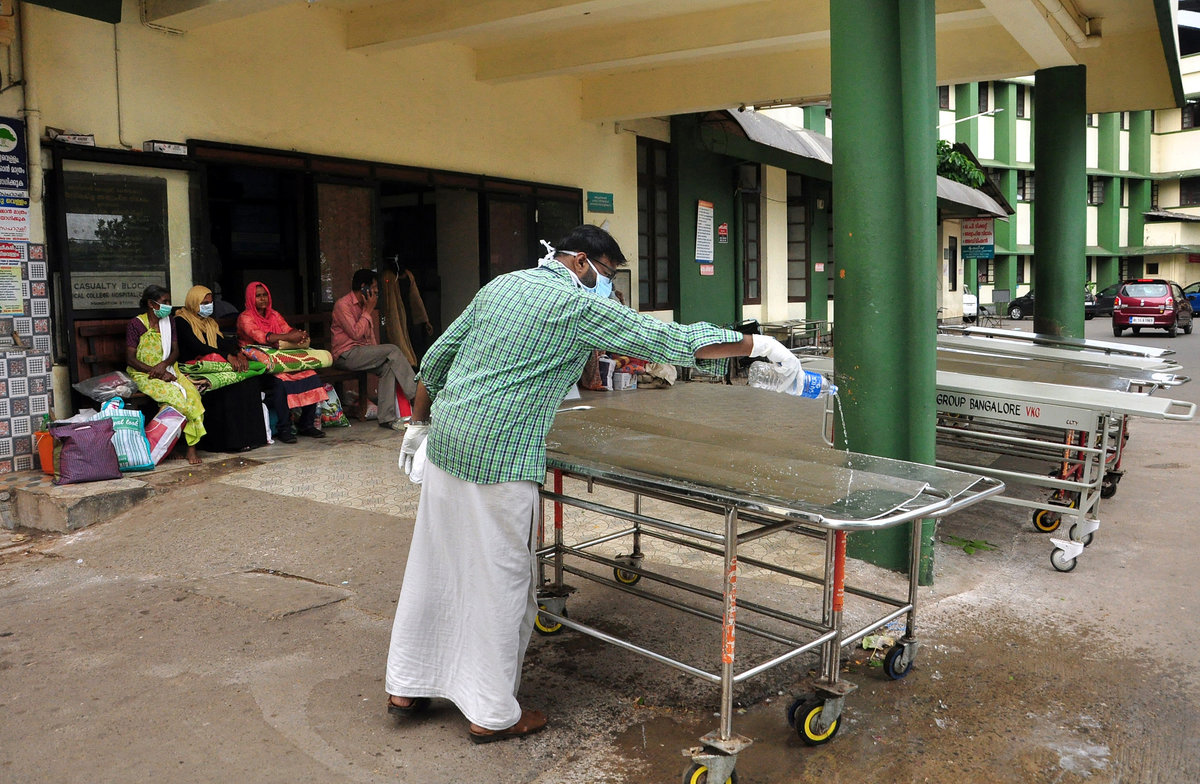
Health officials investigating the outbreak in Kerala, where the first death happened on Friday, have traced it to a well infested with bats from which the victims drew water.
Human-to-human transmission of the virus has been recorded in previous outbreaks in India that killed as many as 50 people.
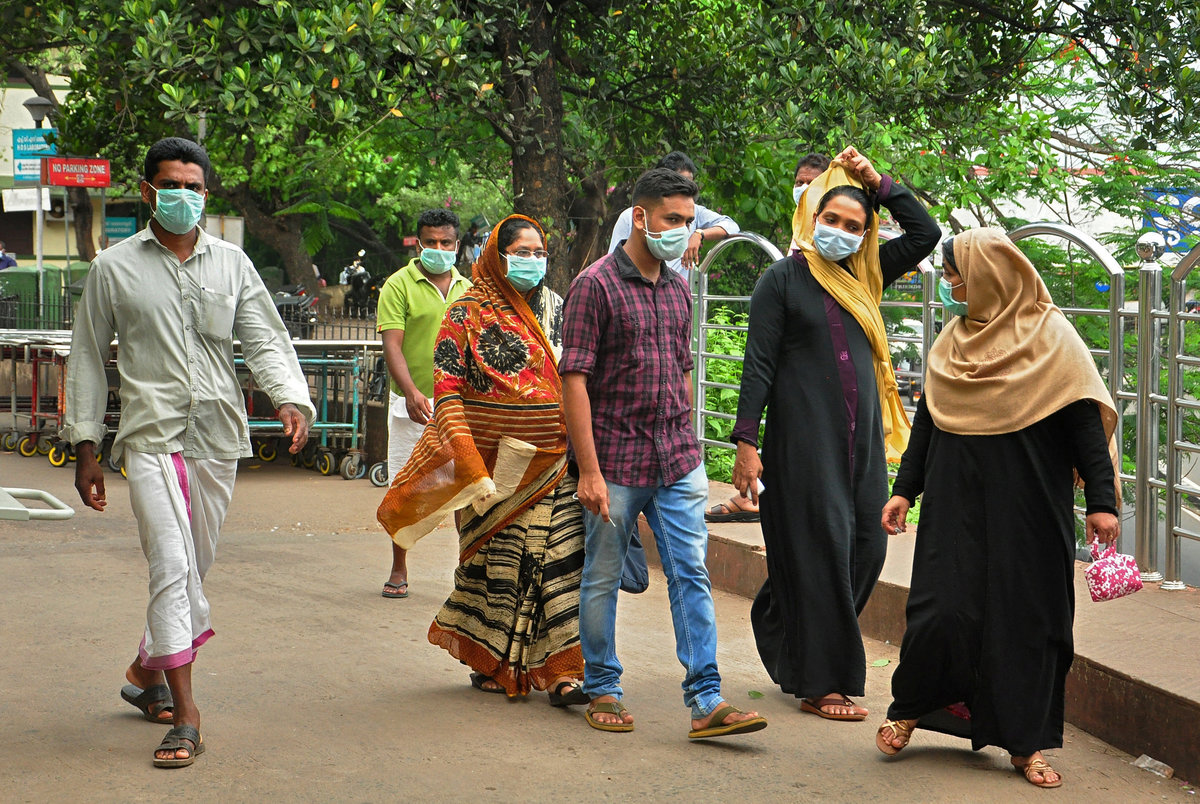

Travel to Kerala, a popular tourist destination, was declared safe by Rajeev Sadanandan, a state health official, who said the outbreak "remains highly localized", with all cases linked to one family.
He declined to comment on the Mangalore cases, but identified the districts of Kannur, Kozhikode, Malappuram and Wayanad for tourists in Kerala to avoid, as being close to the outbreak and under scrutiny by health officials.
"Since there are many foreigners who travel to Kerala, we are advising they can avoid these districts for abundant caution," he told Reuters.
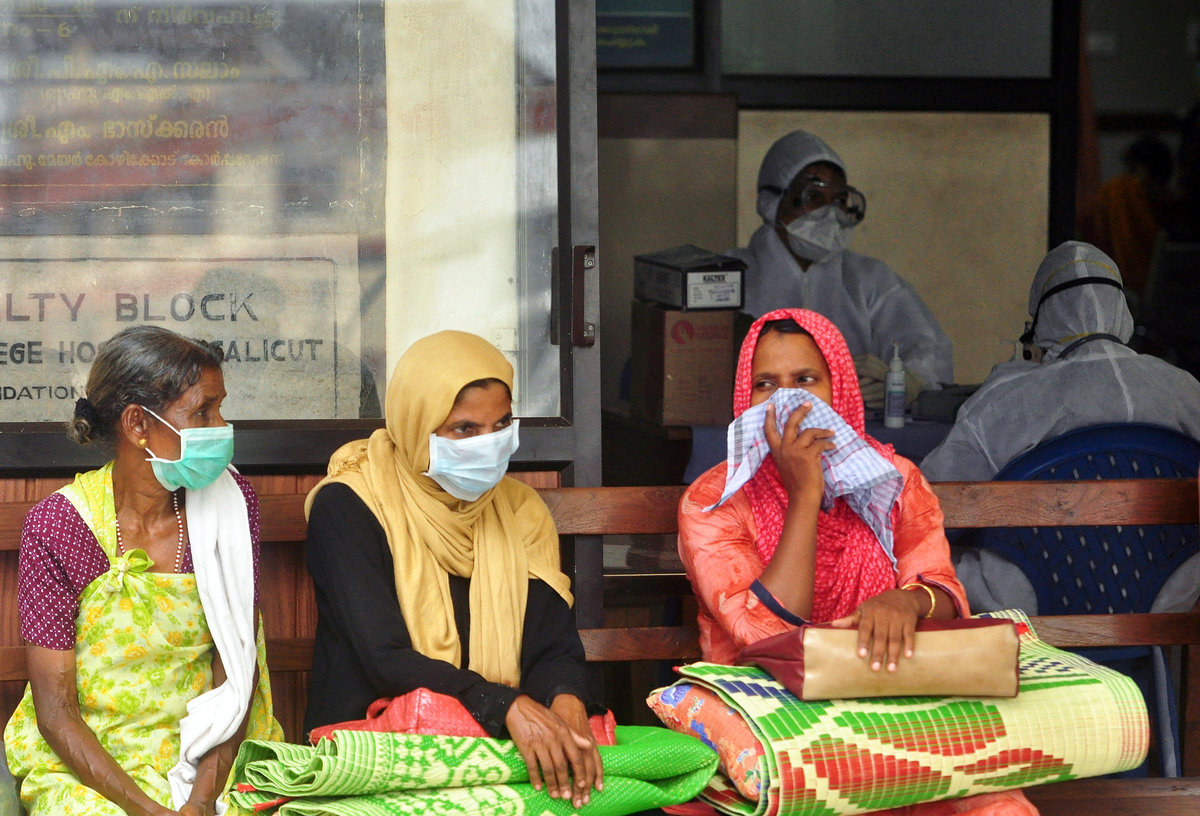

A nurse who treated three of the Kerala victims succumbed to the infection on Monday, Health Minister K.K. Shailaja told a news briefing, where she announced payment of compensation to her family and others who lost family members to the infection.
At least 17 patients are under treatment, Shailaja added.
"All steps to prevent the spread of the virus have been taken," she added, urging people not to destroy colonies of fruit bats.
(Reporting by Zeba Siddiqui in Mumbai and D. Jose in Kochi; Editing by Sanjeev Miglani and Clarence Fernandez)







