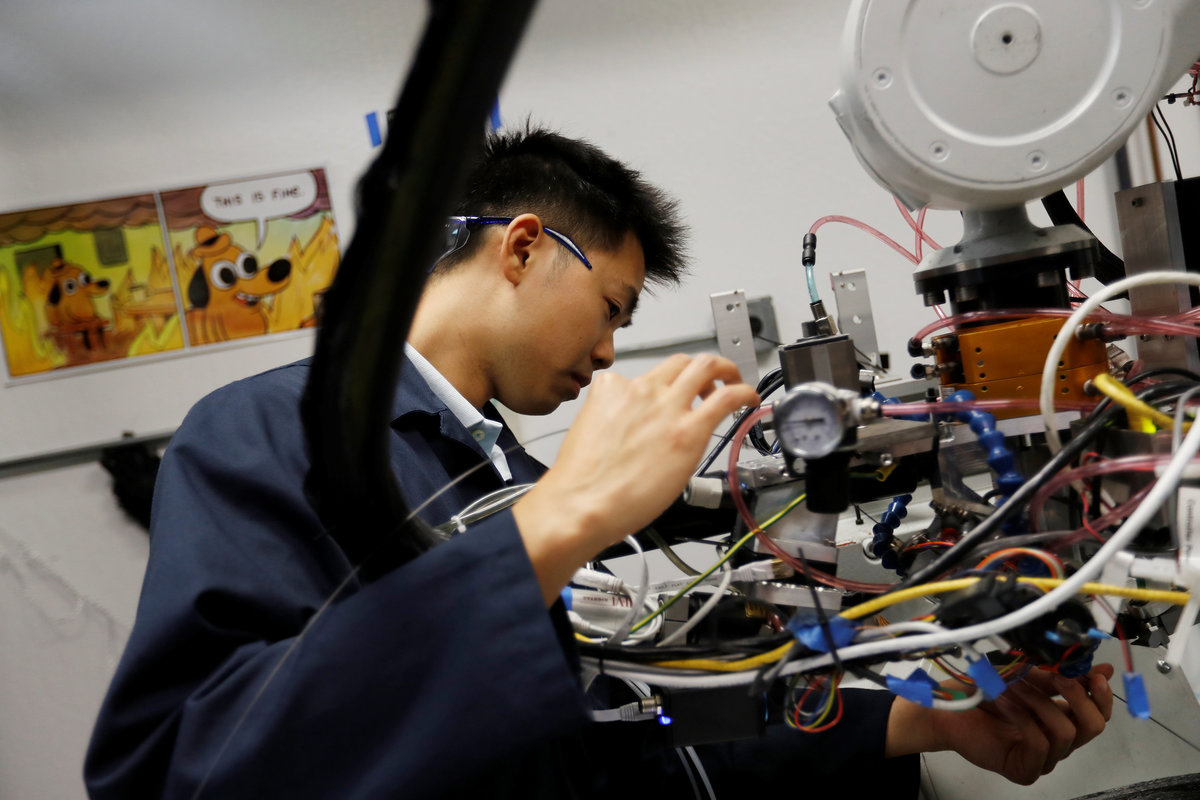
(Reuters) - After a career that included helping Alphabet Inc's Google build out data centers and speeding packages for Amazon.com Inc to customers, Jim Miller is doing what many Silicon Valley executives do after stints at big companies: finding more time to ride his bike.
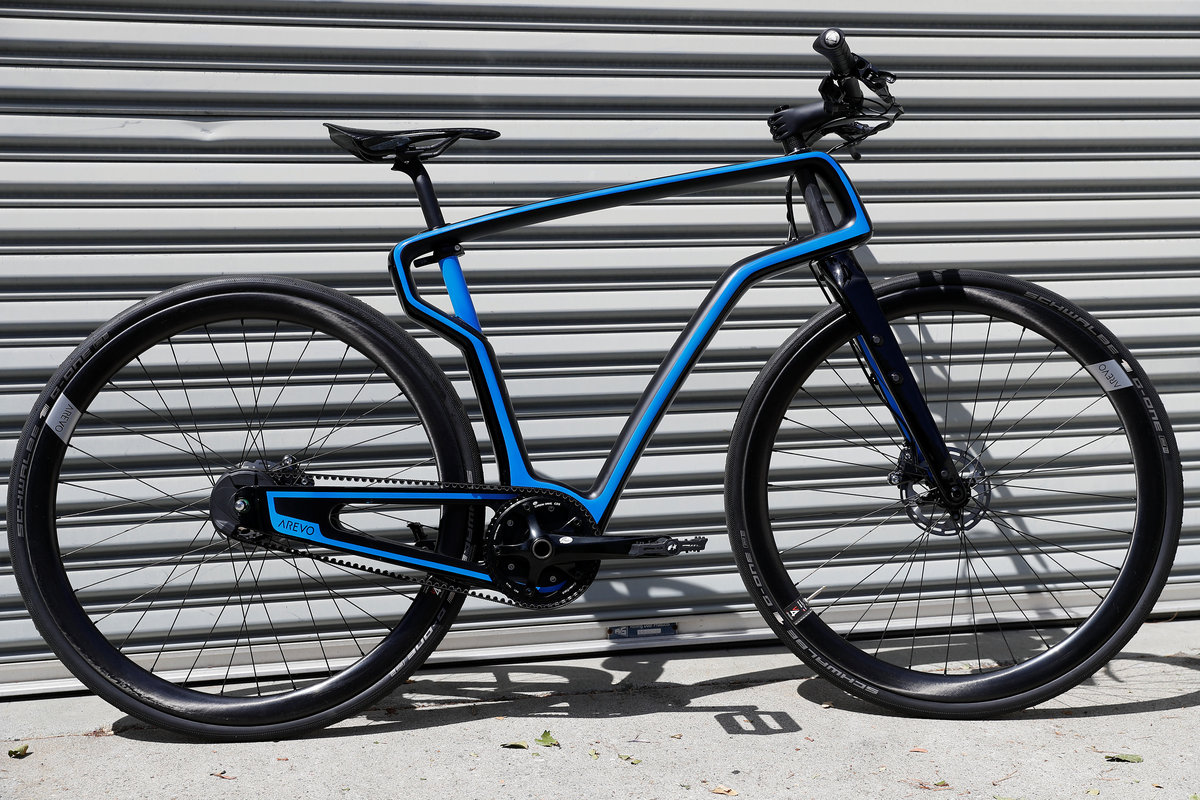
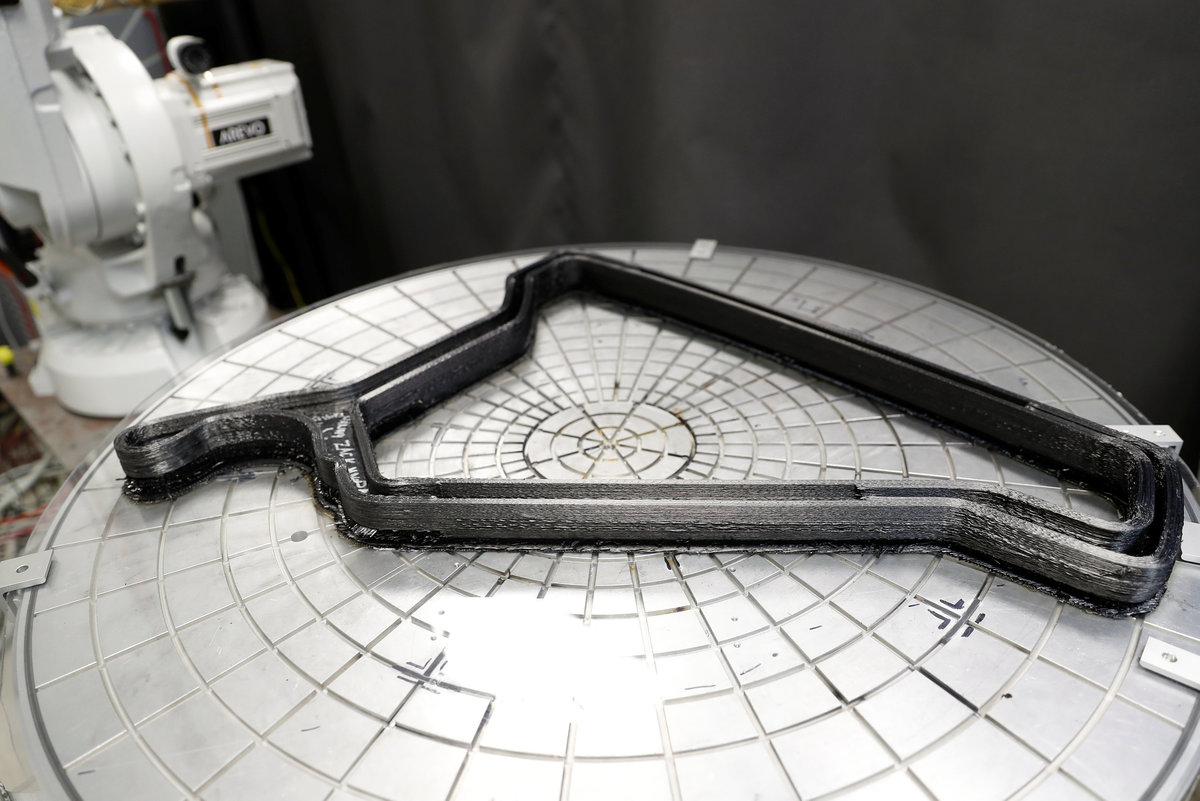
But this bike is a little different. Arevo Inc, a startup with backing from the venture capital arm of the Central Intelligence Agency and where Miller recently took the helm, has produced what it says is the world's first carbon fiber bicycle with 3D-printed frame.
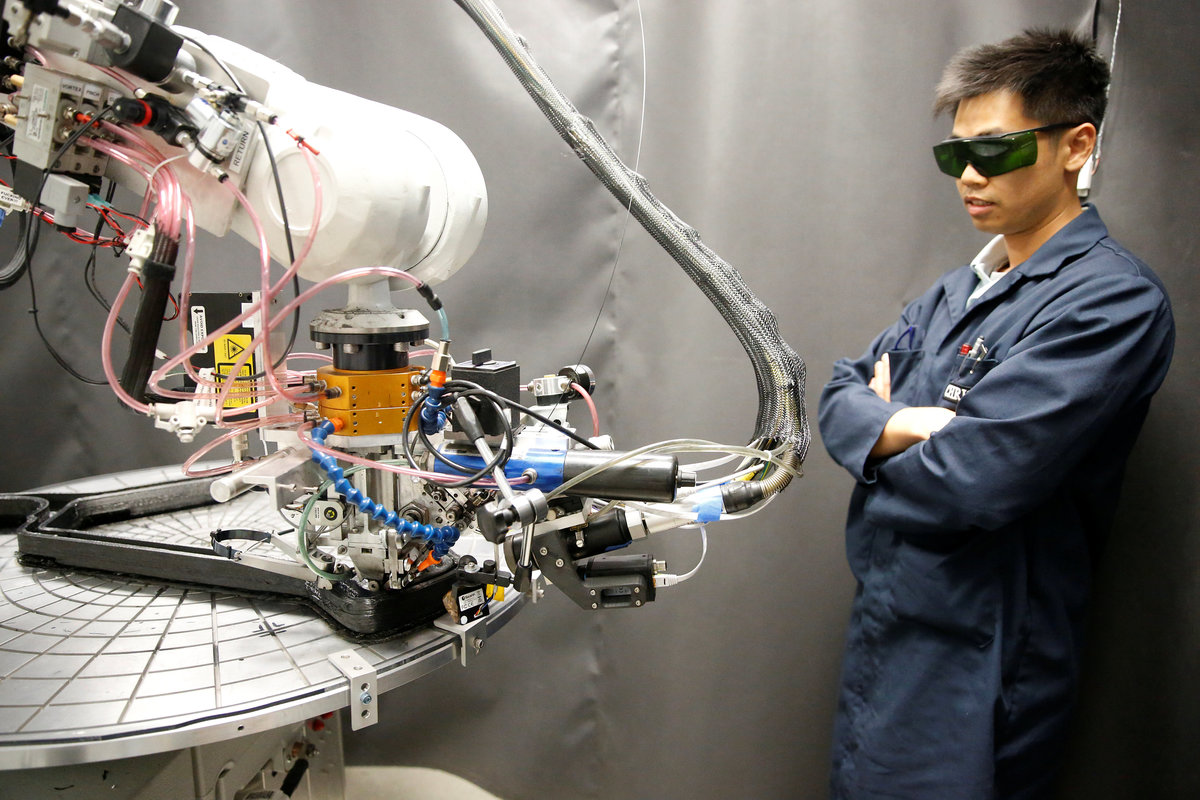
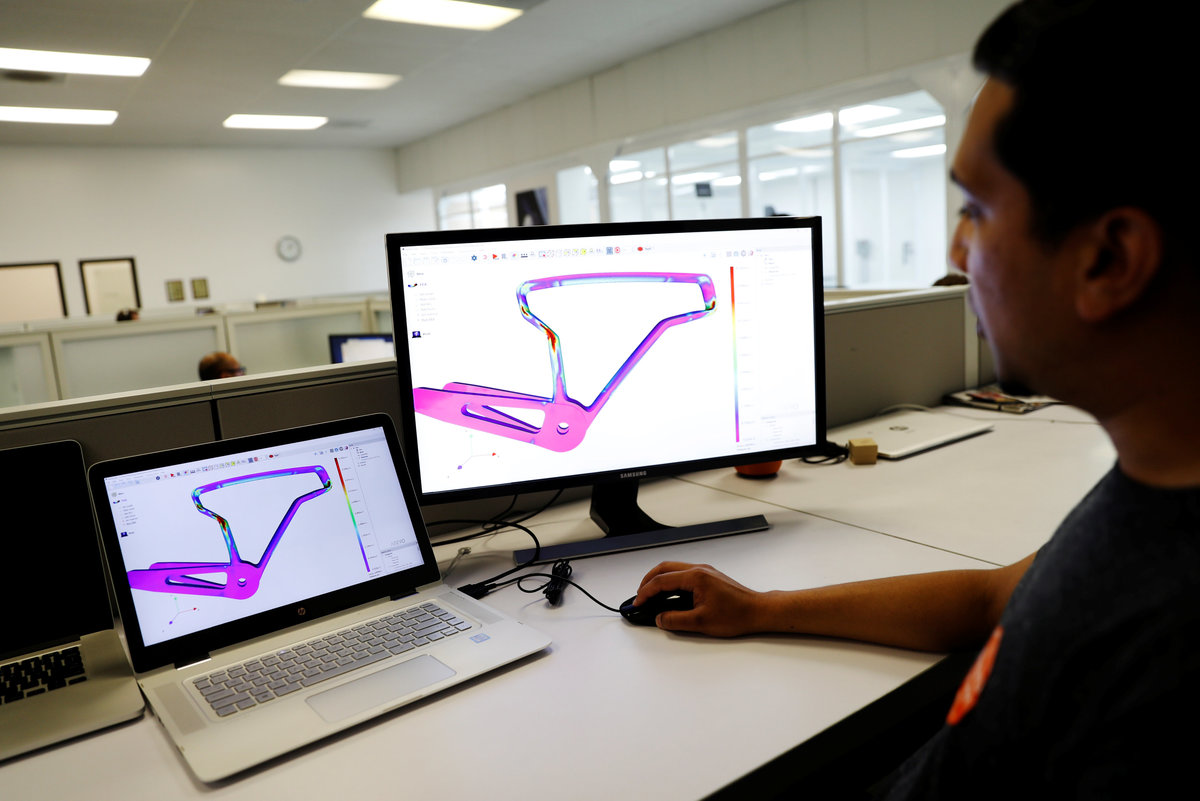
Arevo is using the bike to demonstrate its design software and printing technology, which it hopes to use to produce parts for bicycles, aircraft, space vehicles and other applications where designers prize the strength and lightness of so-called "composite" carbon fiber parts but are put off by the high-cost and labor-intensive process of making them.
Arevo on Thursday raised $12.5 million in venture funding from a unit of Japan's Asahi Glass Co Ltd, Sumitomo Corp's Sumitomo Corp of the Americas and Leslie Ventures. Previously, the company raised $7 million from Khosla Ventures, which also took part in Thursday's funding, and an undisclosed sum from In-Q-Tel, the venture capital fund backed by the CIA.
Traditional carbon fiber bikes are expensive because workers lay individual layers of carbon fiber impregnated with resin around a mold of the frame by hand. The frame then gets baked in an oven to melt the resin and bind the carbon fiber sheets together.

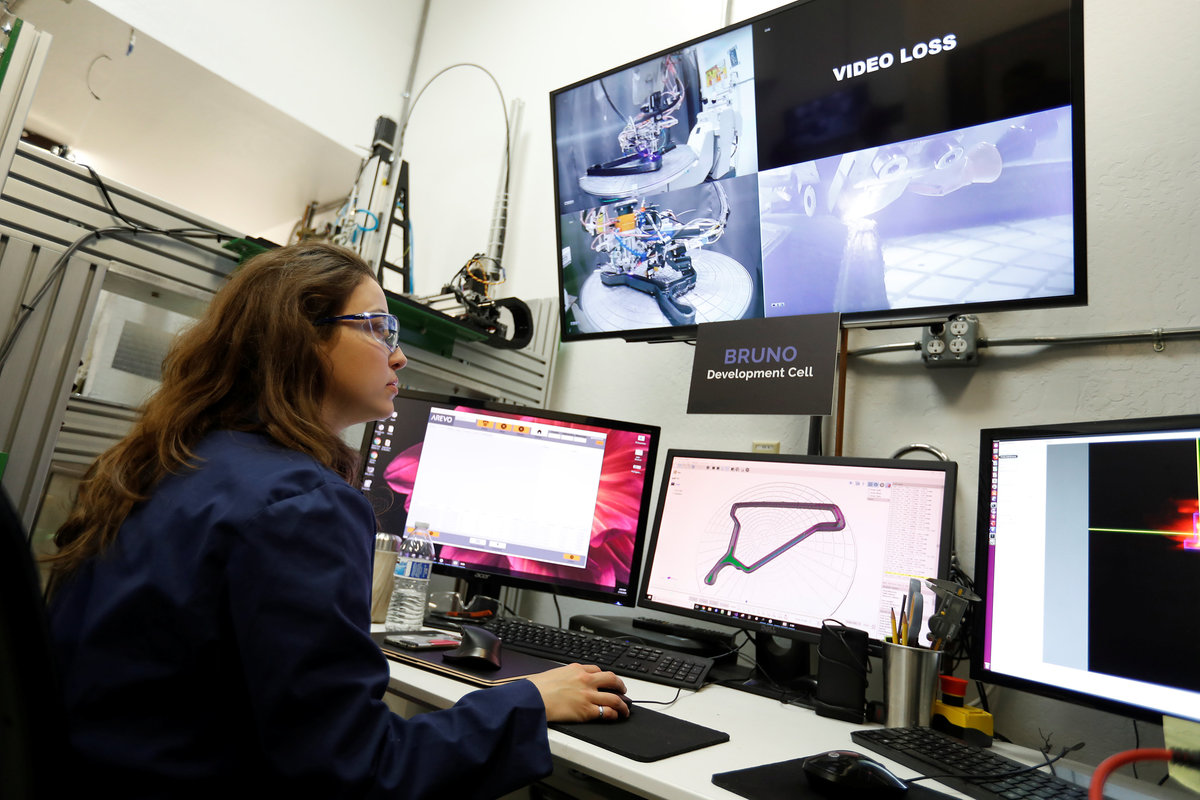
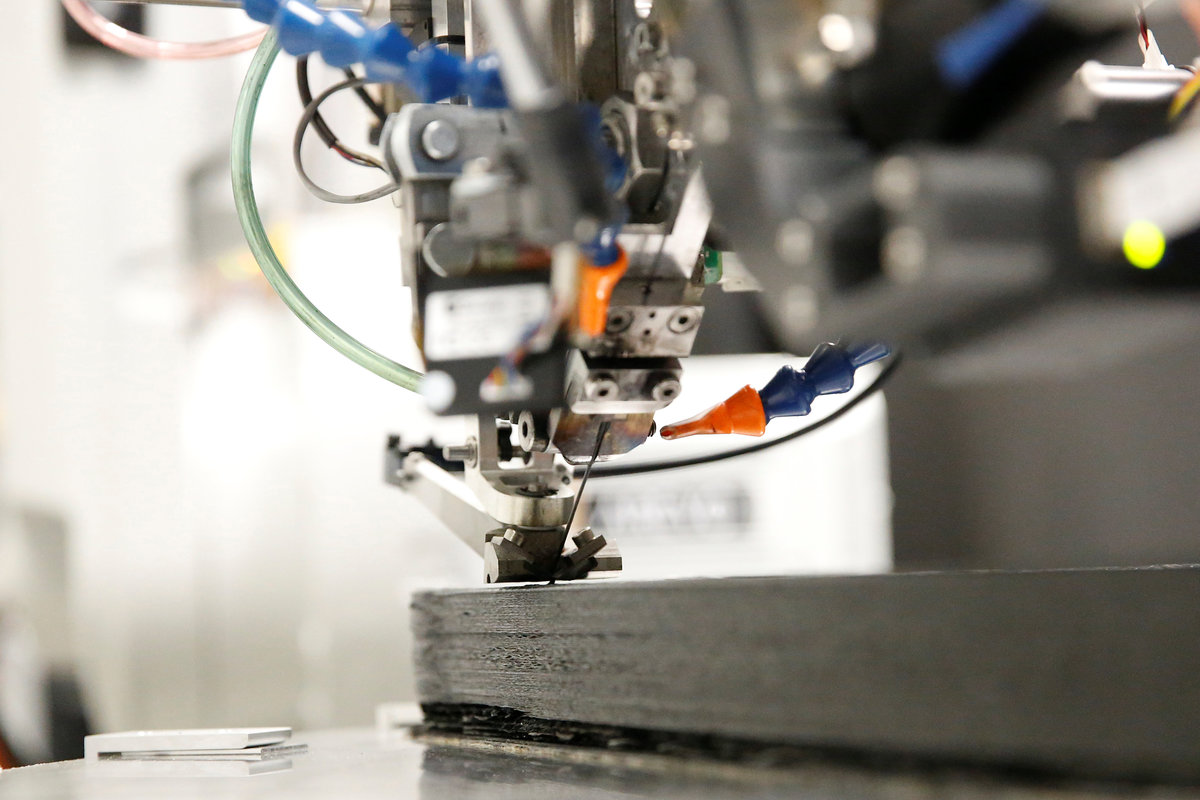
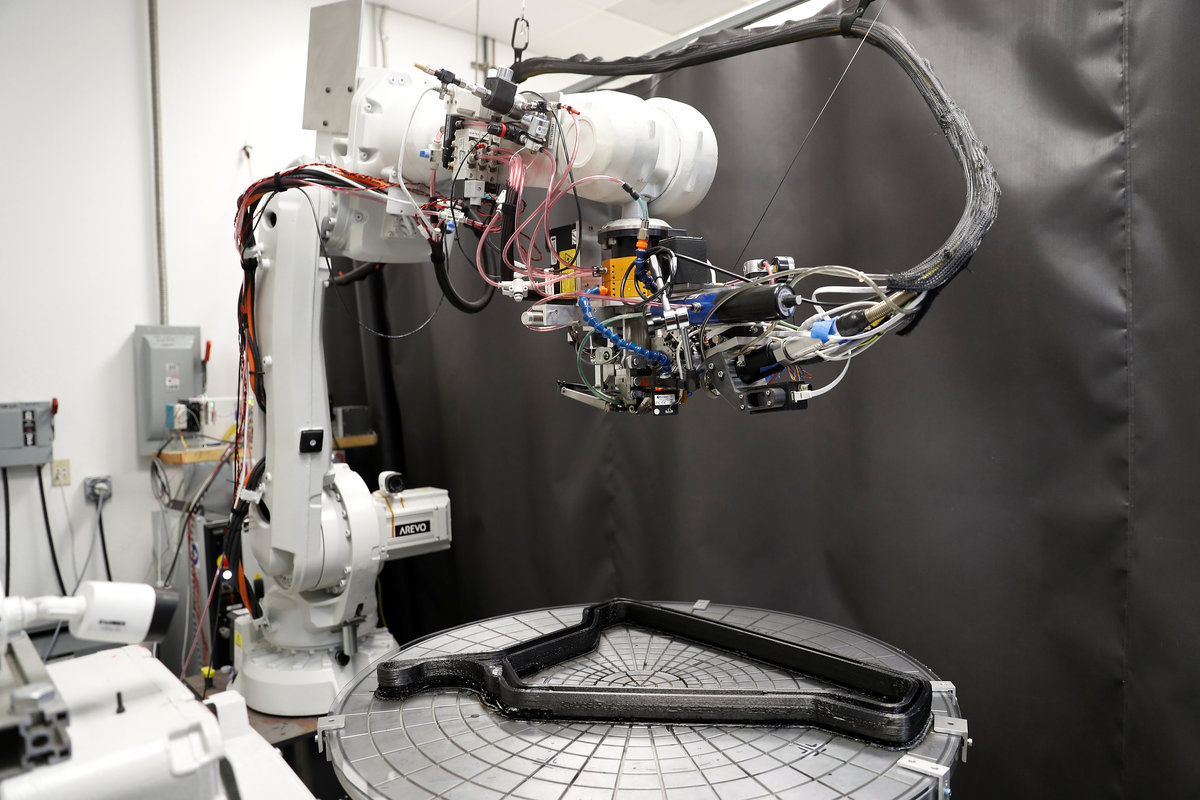
Arevo's technology uses a "deposition head" mounted on a robotic arm to print out the three-dimensional shape of the bicycle frame. The head lays down strands of carbon fiber and melts a thermoplastic material to bind the strands, all in one step.
The process involves almost no human labor, allowing Arevo to build bicycle frames for $300 in costs, even in pricey Silicon Valley.
"We're right in line with what it costs to build a bicycle frame in Asia," Miller said. "Because the labor costs are so much lower, we can re-shore the manufacturing of composites."

While Miller said Arevo is in talks with several bike manufacturers, the company eventually hopes to supply aerospace parts. Arevo's printing head could run along rails to print larger parts and would avoid the need to build huge ovens to bake them in.
"We can print as big as you want - the fuselage of an aircraft, the wing of an aircraft," Miller said.
(Reporting by Stephen Nellis; Editing by Lisa Shumaker)