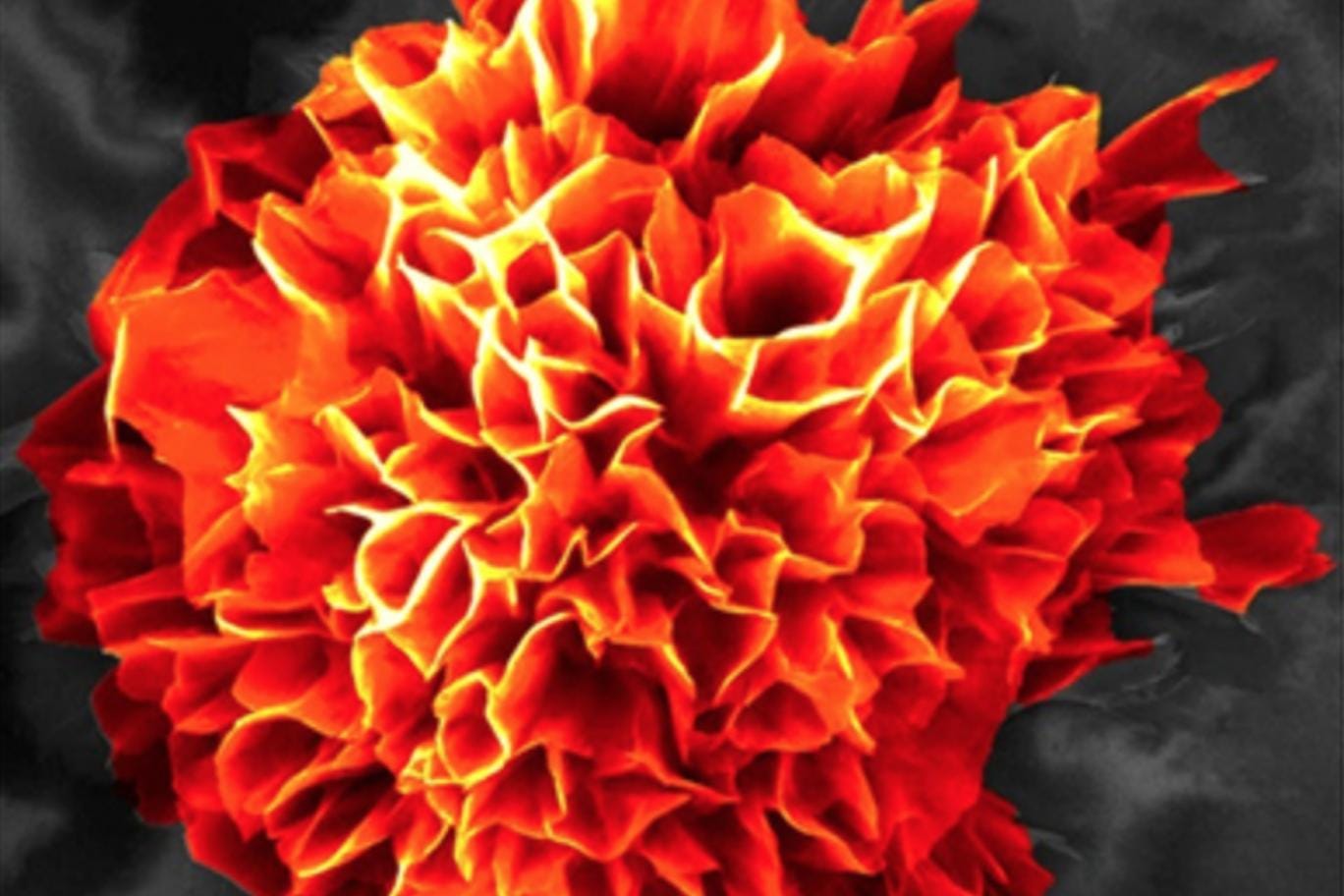
Australian scientists have created artificial flowers that are so small that 10 could fit along the width of a human hair.
The microflowers were created by a team from the RMIT-Indian Institute of Chemical Technology Research Centre, and are actually tiny chemical structures that 'grow' and 'bloom' when they come in contact with water, mimicking the behaviour of real flowers.
Aside from looking pretty amazing, the tiny flowers could have practical applications, in areas like nanotechnology, biomedicine and optoelectronics - the study of electronic devices that detect and control light.
Dr Sheshanath Boshanale, lead investigator on the project, said that while this discovery was still its infancy, it represents an exciting development for the team.
"This is the first time flower-shaped microforms have been developed in a water solution, opening an exciting new pathway for further research," he said. The team's research has since been published in Scientific Reports, a high-profile open journal from the publishers of Nature.
"While tiny, they have potential to make a big impact by enabling researchers to easily and reliably build microflowers and use them to break frontiers in a range of scientific fields," Boshanale added.
To create the microflowers, the researchers simply mixed two organic compounds, phosphonic acid and melamine, in water.
As the water evaporates, the microflowers 'bloom', in a process that takes around three hours.







