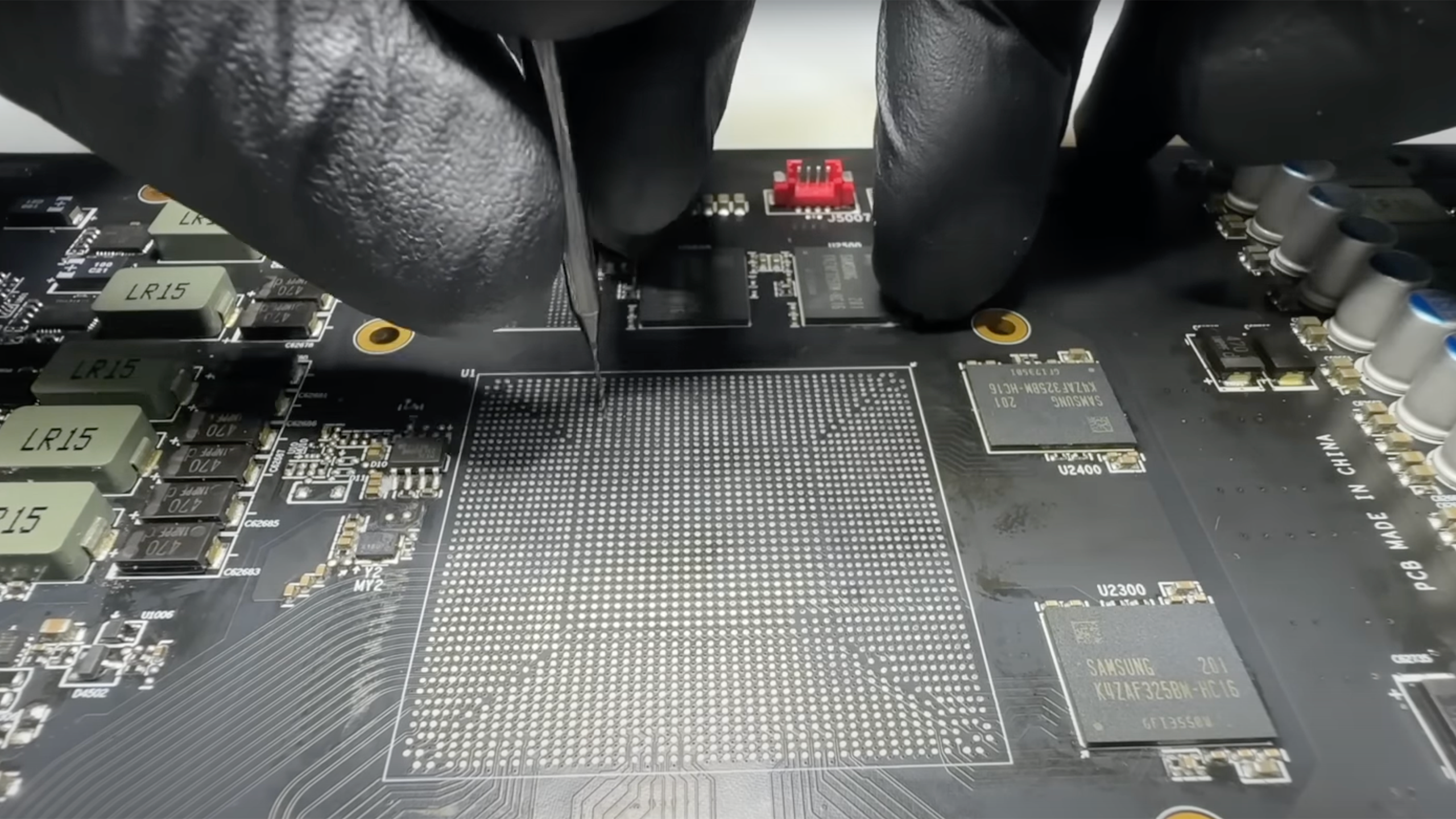
Sometimes, graphics cards break down. Experienced repairmen can quickly identify the issue and either fix it or send the board to a bin, but some problems require an ingenious fix. KrisFix from GPUFix.de is a GPU repair specialist, and he recently encountered a malfunctioning graphics card that required him to drill two holes in the PCB and restore a trace.
This time around KrisFix got an MSI Radeon RX 6900 XT (which is still one of the best graphics cards despite being nearly three years old) with a rare problem where the fans and LEDs work, but there is no picture. The engineer claims that, so far, he has observed this behavior on six or seven graphics cards out of hundreds he has fixed. The source of the problem was a broken trace between the GPU and a memory chip, which in some cases led to the complete malfunctioning of a GPU.
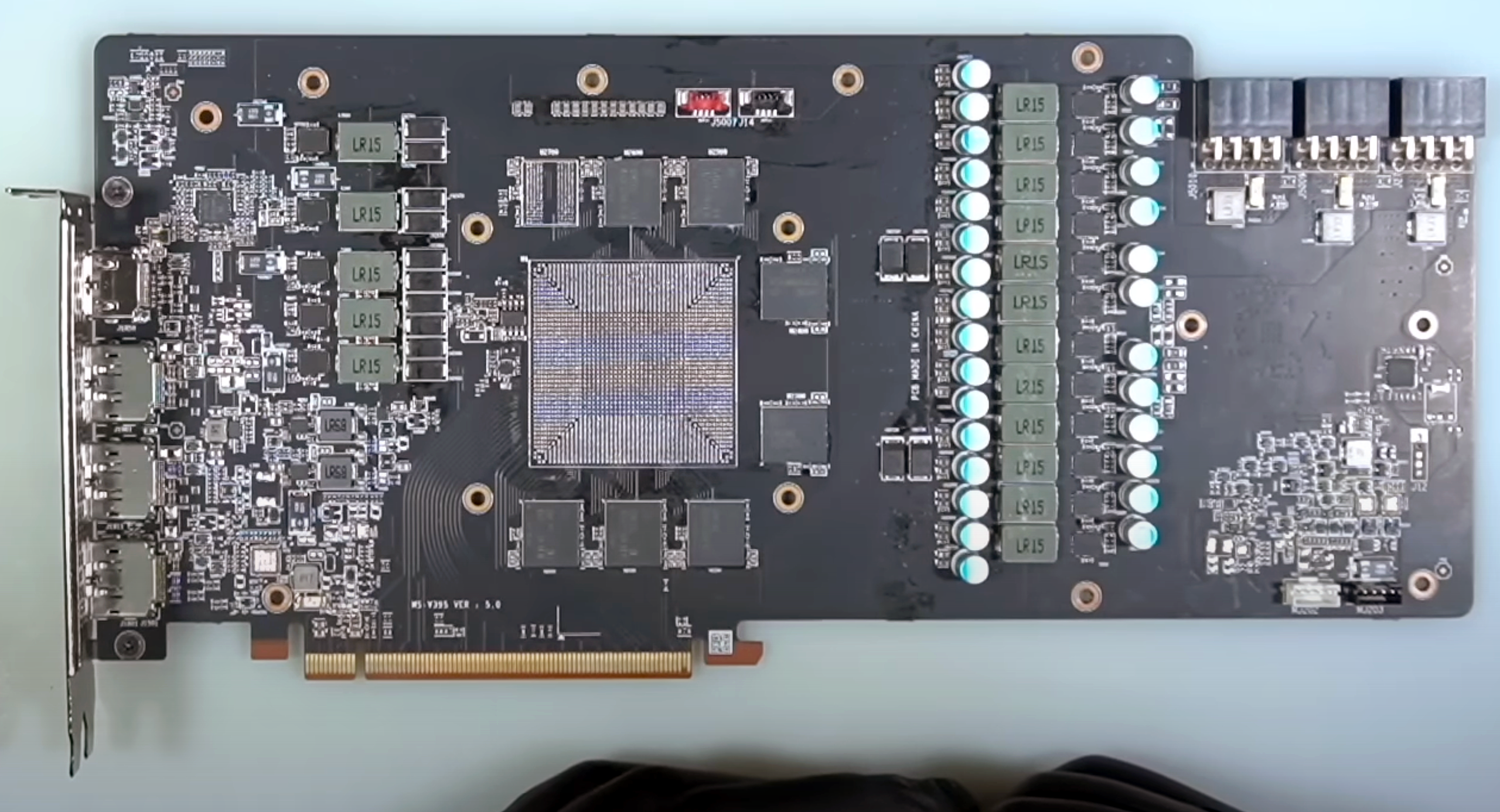
Modern high-end video cards are highly complex devices using printed circuit boards with 15 layers. Fixing a broken trace that resides deep inside the PCB is a challenge, to say the least, and the broken trace is located on the layer deep underneath the surface, eliminating almost any possibility of fixing it in a reasonable amount of time. Instead, KrisFix had to rebuild it using a wire by drilling two holes in the graphics card, solder a tiny wire to a pin on the memory soldering pad, solder it to a pin on the GPU soldering pad, and solder the DRAM chip and the GPU back.
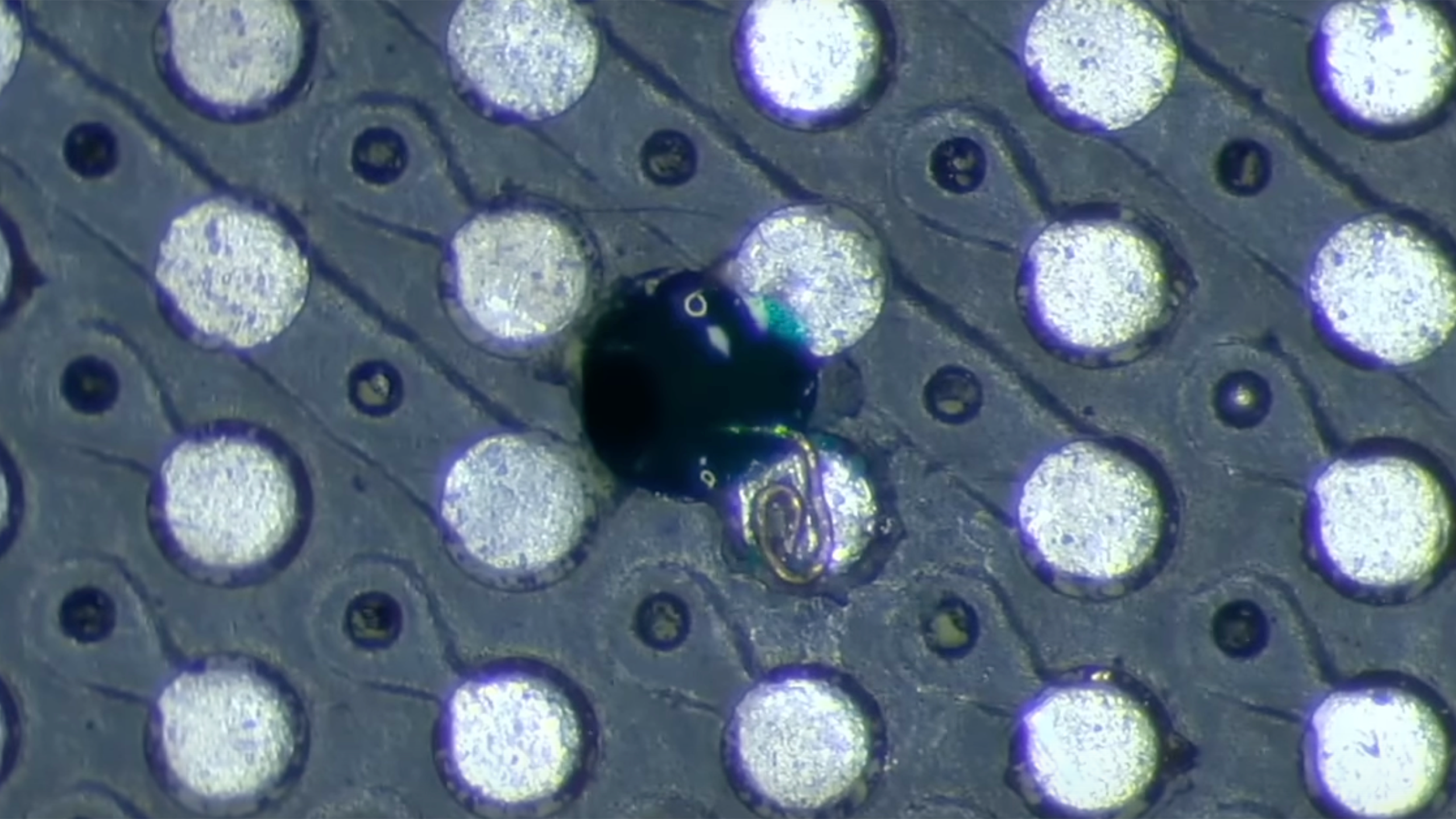
Drilling a hole in an enthusiast-grade graphics card, such as MSI's Radeon RX 6900 XT, is a precise and delicate process that KrisFix prefers to do by hand. This whole process requires extreme precision and the use of a microscope to solder the hole, solder wires, resolder damaged capacitors, and restore broken traces on top of the PCB that got scratched during the process.
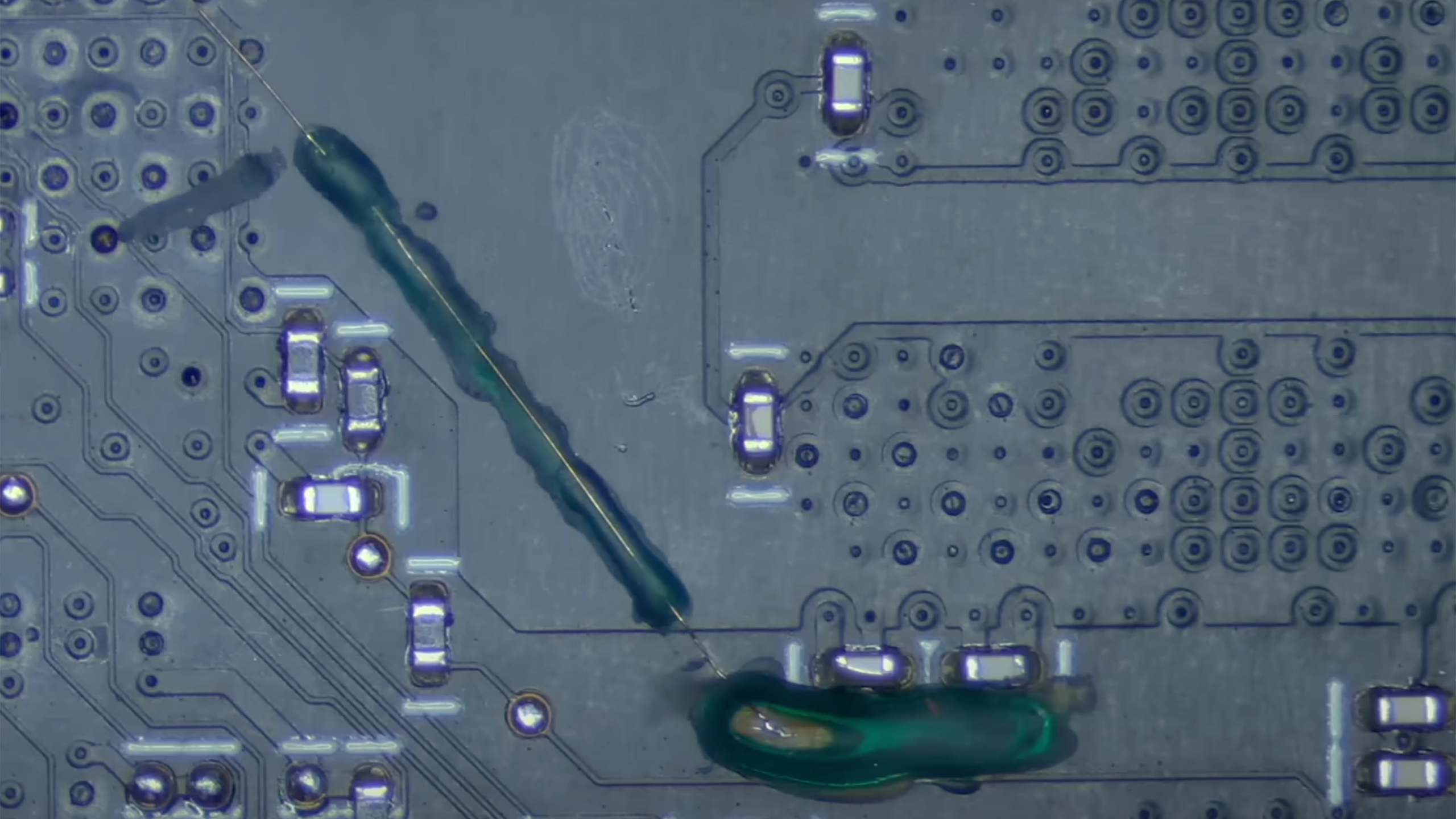
The procedure performed by KrisFix is certainly an extraordinary one, and we assume that the stability of the board's operation was sound. However, the video report does not touch upon whether the manipulation of the memory trace length affects performance. Both GDDR5 and GDDR6 standards support read and write training sequences to ensure signal integrity, compensate for signal variabilities, and optimize timings. Timings were certainly affected by the trace length, though it is unclear how and how this affects performance in real-world games.
While repairmen are not in the business of drilling holes in graphics boards because this tends to damage them, in some cases, drilling holes can actually give life to a video card that is seemingly gone.







