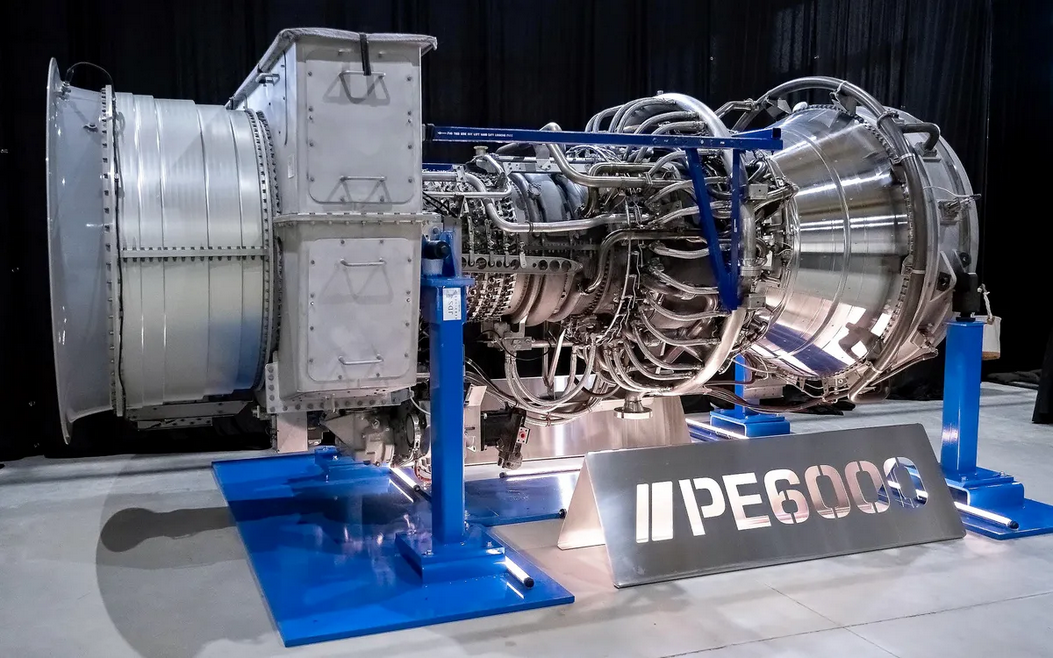
Faced with multi-year delays to secure grid power, US data center operators are deploying aeroderivative gas turbines — effectively retired commercial aircraft engines bolted into trailers — to keep AI infrastructure online.
According to IEEE Spectrum, facilities in Texas are already spinning up units based on General Electric’s CF6-80C2 and LM6000, the same turbine cores once found on 767s and Airbus A310s. Vendors like ProEnergy and Mitsubishi Power have turned these into modular, fast-start generators capable of delivering 48 megawatts apiece, enough to support a large AI cluster while utility-scale infrastructure lags.
Fast, loud, and anything but elegant, these “bridging power” units come from vendors like ProEnergy, which offers trailerized turbines built around ex-aviation cores that can spin up in minutes to meet energy demand. Meanwhile, Mitsubishi Power’s FT8 MOBILEPAC, which derives from Pratt & Whitney jet engines, delivers a similar output in a self-contained footprint designed for fast deployment.
While this might not be the cheapest, and certainly not the cleanest, way to power racks, it’s a viable stopgap for companies racing to hit AI milestones while local substations and modular nuclear power deployments remain years away.
Jet-derived turbines are nothing new. They’ve been used in military and offshore drilling operations for decades, but this is the first time they’ve appeared in any meaningful way at data center sites. That speaks volumes about just how tight power supplies in the U.S. have become.
In one of the more visible examples, OpenAI’s parent group is deploying nearly 30 LM2500XPRESS units at a facility near Abilene, Texas, as part of its multi-billion-dollar Stargate project. Each unit spins up to 34 megawatts, fast enough to cold-start servers in under ten minutes.
What they gain in fast deployment and ramp speed, they lose in thermal efficiency. Aeroderivative turbines run in simple-cycle mode, burning fuel without capturing waste heat, which puts them well below the efficiency of combined-cycle plants. Most run on diesel or gas delivered by truck, and require selective catalytic reduction to meet NOx limits.
Still, it’s not difficult to see the appeal. Even a small AI buildout can demand 100 megawatts or more, and with some utilities quoting lead times of five years or more, we should expect to see more stopgap power generation being implemented to meet burgeoning AI power demands.
Follow Tom's Hardware on Google News, or add us as a preferred source, to get our latest news, analysis, & reviews in your feeds.








