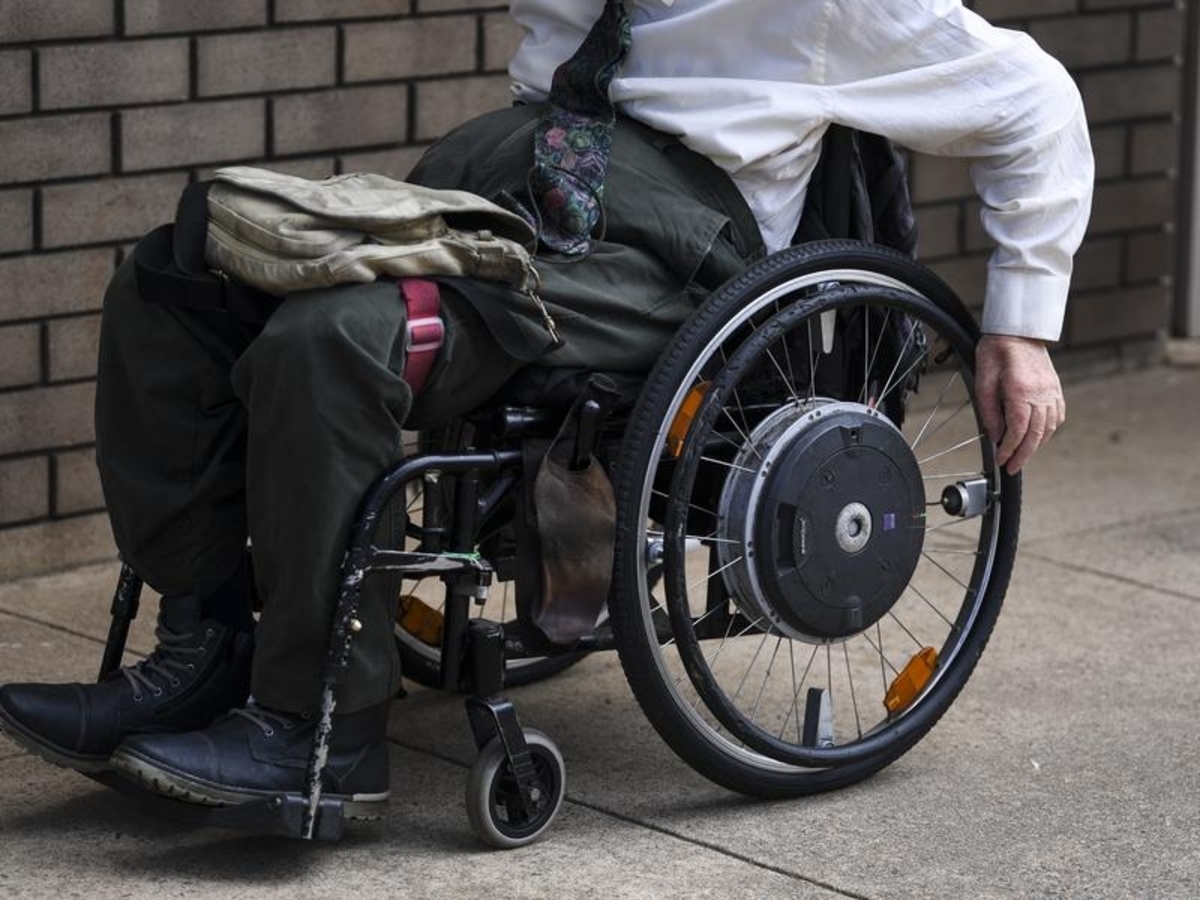
Australians paralysed by spinal injury could soon move and walk again, if an Australian clinical trial exploring a neurological treatment is successful.
Led by researchers at Neuroscience Research Australia (NeuRA) the landmark international trial aims to restore function of remaining spinal nerves through neurostimulation.
The therapy sends electrical impulses through electrodes attached to the skin over the spinal cord, and when coupled with step and walking training, is hoped to help rewire the neural pathways in people with chronic paraplegia.
"Neurostimulation is like a hearing aid for the spinal cord," the study's lead researcher Professor Simon Gandevia, also the Deputy Director of NeuRA, says.
"The idea is that tailored electrical currents can amplify messages transmitted via surviving neural pathways, thereby enhancing communication between the brain and the body.
Professor Gandevia says the results of previous small neurostimulation studies are compelling and positive, but a lack of solid clinical trials have thus far prevented the treatment from making it to the market.
"Volunteers in research overseas have even been able to stand and walk," he said.
"However, until now, researchers have not been able to test this promising technology in a clinical setting,"
Patients in Sydney, Chicago, Glasgow and Toledo are taking part in the trial, with initial results expected in 18 months.
But with more than 20,000 Australians living with paralysis, NeuRA and SpinalCure Australia hope it could be expanded to focus on restoring other bodily functions too.
"The impact of a spinal cord injury is life-shattering, and there is no treatment, pill or lifestyle change that can mitigate its effects," SpinalCure Australia chief executive Kathryn Borkovic said.
"Loss of movement is just the tip of the iceberg - ongoing pain, digestive health issues, pressure sores, spasm, loss of bladder and bowel control and impaired sexual function are just some of the effects that can make everyday life so difficult."
They're calling on the federal government to chip in funding, with at least another $20 million needed to expand the research.