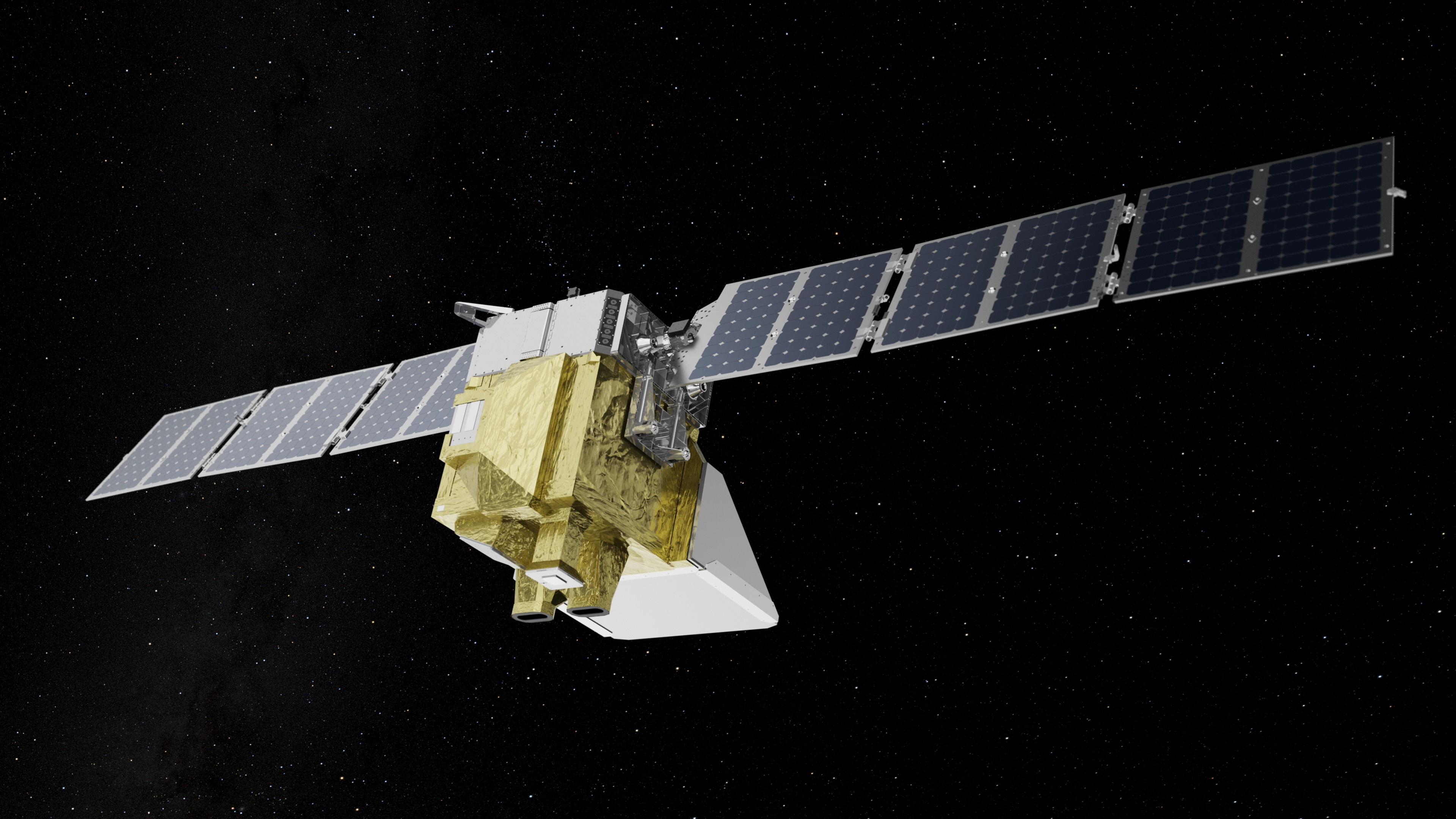
One of the most advanced satellites for tracking harmful greenhouse gas emissions has died in space.
MethaneSAT, built and operated by the nonprofit Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), was launched in March of 2024 as part of SpaceX's Transporter-10 mission. The spacecraft was designed to pinpoint methane hotspots across the globe — specifically, those created by oil and gas production — and provide freely accessible data analytics about specific emission sources.
Now, after a year of collecting that data, the satellite is no longer operational. "On Friday, June 20, the MethaneSAT mission operations lost contact with MethaneSAT. After pursuing all options to restore communications, we learned this morning that the satellite has lost power, and that it is likely not recoverable," EDF said in a statement on Tuesday (July 1).
Though invisible, methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases. Methane molecules absorb infrared radiation very efficiently, trapping 20 to 30 times more heat in Earth's atmosphere when compared to carbon dioxide. Fossil fuel production and industrial waste are some of the highest human-related contributors of methane into the atmosphere. That methane then hovers in Earth's troposphere — about five to nine miles (eight to 15 kilometers) in altitude — like a warm coat around the planet.
MethaneSAT was designed as a sort of check against commercial climate measurements in order to help policymakers independently verify industry emissions reports. "MethaneSAT is specifically designed to catalyze methane reductions by creating unprecedented transparency," the mission's website states.
EDF lists 10 mission partners credited with bringing the $88 million satellite to fruition, including BAE Systems, Harvard University, the New Zealand Space Agency, Bezos Earth Fund, Google and more. Though MethaneSAT is now out of service, mission operators say they're still committed to turning the data they were able to collect into actionable results.
"We will continue to process data that we have retrieved from the satellite and will be releasing additional scenes of global oil and gas production region-scale emissions over the coming months," EDT officials said. "To solve the climate challenge requires bold action and risk-taking and this satellite was at the leading edge of science, technology and advocacy. "