If you’re new to astrophotography, you’ve timed it well because January is one of the best months to begin. If you can find clear skies in the northern hemisphere, then there’s a nice mix of objects to image, from the likes of the Orion Nebula (M42) and the Pleiades (M45) to the Quadrantids meteor shower, the rise of the full ‘Wolf Moon,’ and a young crescent moon.
Here’s everything you need to know about astrophotography this month:
3-4 January: Quadrantids meteor shower
The Quadrantids are an underrated meteor shower, with as many as 60 meteors per hour and a strong possibility of bright ‘fireballs.’ If you want to get outside with your camera to attempt long exposure images of shooting stars, do so before the moon rises after midnight.
Read: How to photograph a meteor shower
4 January: Dark sky window opens
Today, the moon is half-lit from our perspective, called the Last Quarter or Third Quarter Moon. It will rise after midnight, and each night, it will rise around 50 minutes later than the previous night. It means dark, moonless evenings for the next 10 days, perfect for astrophotography. After the New Moon on Thursday, 11 January, the moon will become brighter and bleach the early evening sky.
Read: The best cameras for astrophotography.
8 January: Venus and a crescent moon
You’ll need to wake up an hour before sunrise to catch the classic sight of a slender, waning crescent moon sliding close to the brightest planet in the sky. Our satellite will be just 11% lit and display ‘Earthshine’ – sunlight reflected off Earth’s oceans and ice-caps back onto the lunar surface. Look towards the southeast.
Read: When to photograph the moon
9 January: Mercury and a crescent moon
If you drag yourself out of bed for a second successive morning, a slightly more challenging shot awaits you. This morning, again an hour before sunset, the moon will be just 5% lit, and this time will be just to the right of Mercury. However, they will be much lower on the horizon than yesterday’s planetary action.
12 January: A slender crescent moon
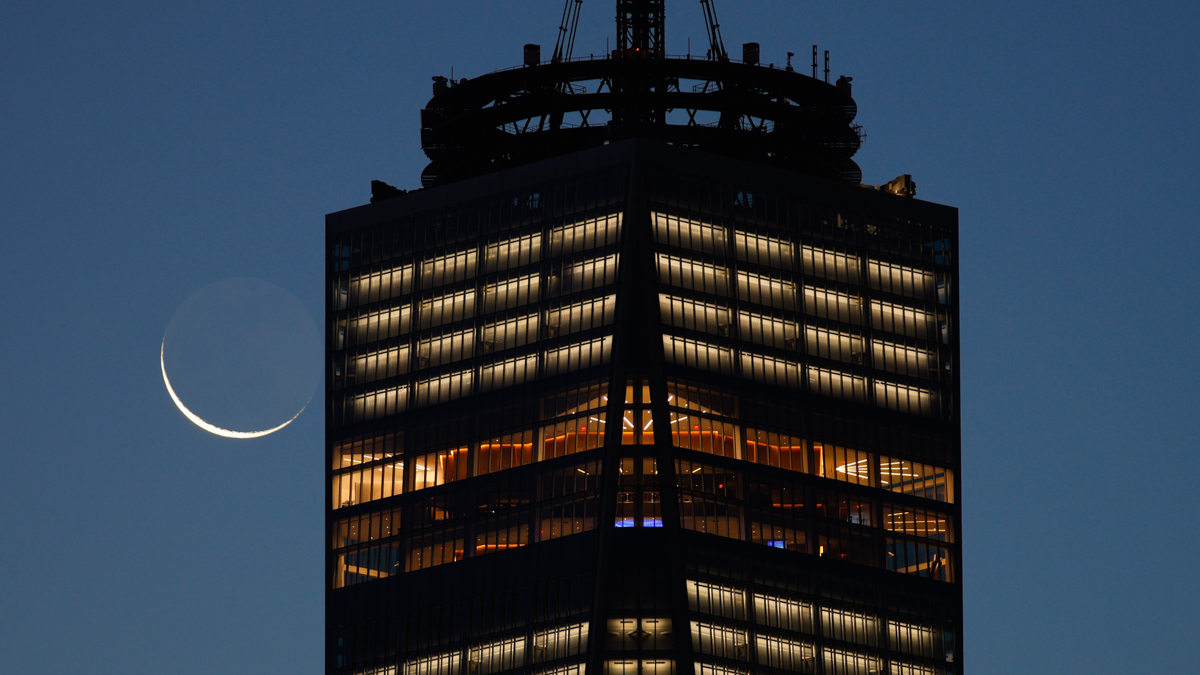

There’s only one occasion each month to capture the youngest, slimmest moon possible. It comes the evening following the New Moon, as the moon emerges from the sun’s glare. Today, the moon will be just 3% lit tonight, so faint that to see it above the southwest horizon will take a pair of binoculars. You’ll also need to be quick because it will set within an hour of sunset. Be careful not to start using binoculars and cameras until the sun has set. If you fail, try again tomorrow when an 8% lit crescent moon will be just as beautiful but more straightforward to find and photograph.
25 January: the rise of the full ‘Wolf Moon’
To capture the moment the full moon appears above the horizon, you must be in the right place at the right time with the right camera gear. You’ll need a camera with a 70-300mm lens, a tripod, and a remote shutter release. Check the time of moonrise where you are and be ready to look east from somewhere with an unobstructed view. Experiment with short exposures and ensure a clear view of the horizon.
Read: How to photograph the full moon
Shot of the month: Daytime moon
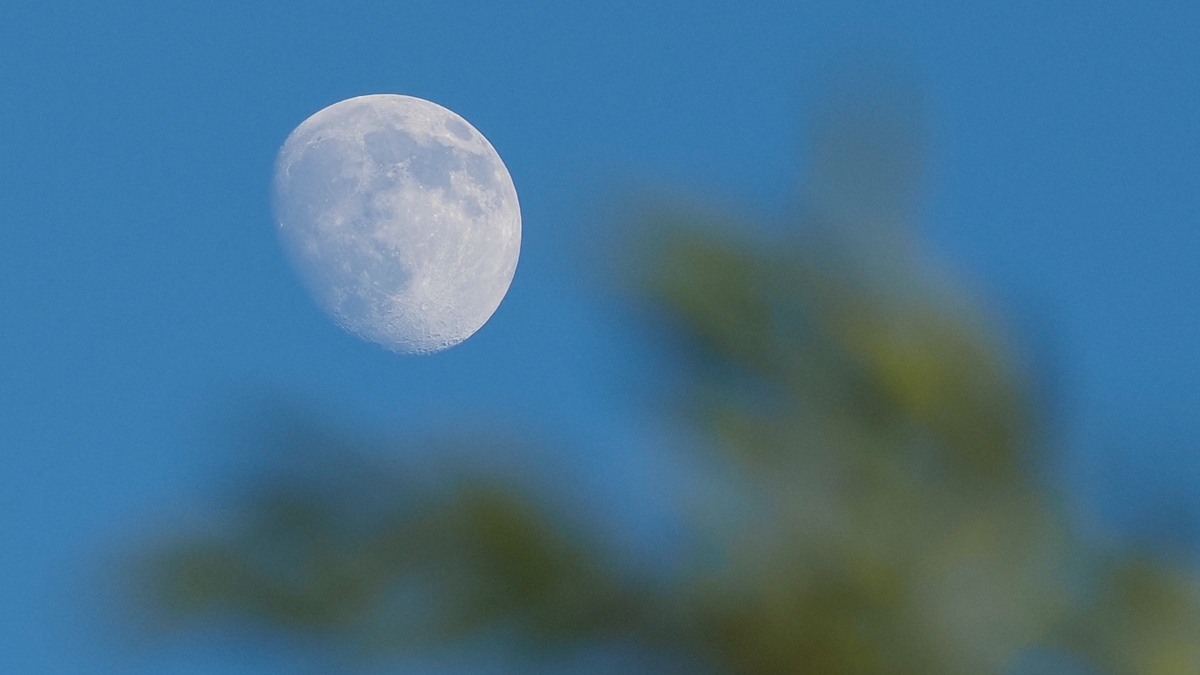

Most people think the moon is only visible at night. It’s actually in the daytime sky just as often as in the night sky and can be photographed shining brightly—if you know when and where.
Our satellite rises about 50 minutes later each day. That means it’s already in the sky, close to the horizon, in the east dusk in the few days before the full moon (try Tuesday, 23 and Wednesday, 24 January). It also means it’s still in the morning sky, close to the horizon, in the west after sunrise in the few days after the full moon (try Friday, 26 to Sunday, 28 January).
Using a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual settings, a telephoto lens, and a tripod, take some time to focus on the moon. Use a fast shutter speed. You’ll need to tweak the settings as the moon gets closer to the horizon, losing brightness as it does so, though the shot you want is the moon in daylight close to some foreground elements. Mountains work very well, as do skyscrapers.
Read more:
Astrophotography: How-to guides, tips and videos
Astrophotography tools: the best camera, lenses and gear
The best star tracker camera mounts
The best light pollution filters